 each pt varies in intensity
each pt varies in intensity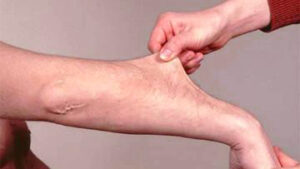

What is Ehlers-Danlos syndrome?
Ehlers-Danlos syndrome is a group of inherited disorders that affect your connective tissues — primarily your skin, joints and blood vessel walls. Connective tissue is a complex mixture of proteins and other substances that provide strength and elasticity to the underlying structures in your body.
People who have Ehlers-Danlos syndrome usually have overly flexible joints and stretchy, fragile skin. This can become a problem if you have a wound that requires stitches, because the skin often isn’t strong enough to hold them.
A more severe form of the disorder, called vascular Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, can cause the walls of your blood vessels, intestines or uterus to rupture. Because vascular Ehlers-Danlos syndrome can have serious potential complications in pregnancy, you may want to talk to a genetic counselor before starting a family.
Symptoms of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome:
There are many different types of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, but the most common signs and symptoms include:
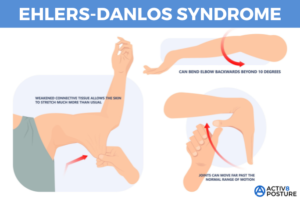
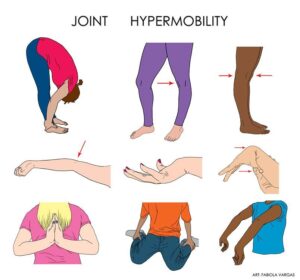
- Overly flexible joints. Because the connective tissue that holds joints together is looser, your joints can move far past the normal range of motion. Joint pain and dislocations are common.
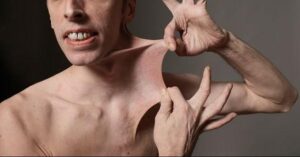
- Stretchy skin. Weakened connective tissue allows your skin to stretch much more than usual. You may be able to pull a pinch of skin up away from your flesh, but it will snap right back into place when you let go. Your skin might also feel exceptionally soft and velvety.
- Fragile skin. Damaged skin often doesn’t heal well. For example, the stitches used to close a wound often will tear out and leave a gaping scar. These scars may look thin and crinkly.
Symptom severity can vary from person to person and depends on the specific type of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome that you have. The most common type is called hypermobile Ehlers-Danlos syndrome.
Vascular Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
People who have vascular Ehlers-Danlos syndrome often share distinctive facial features of a thin nose, thin upper lip, small earlobes and prominent eyes. They also have thin, translucent skin that bruises very easily. In fair-skinned people, the underlying blood vessels are very visible through the skin.
Vascular Ehlers-Danlos syndrome can weaken your heart’s largest artery (aorta), as well as the arteries to other regions of your body. A rupture of any of these larger blood vessels can be fatal. The vascular type can also weaken the walls of the uterus or large intestines — which also may rupture.
Causes:
Different types of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome are associated with a variety of genetic causes, some of which are inherited and passed on from parent to child. If you have the most common form, hypermobile Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, there’s a 50% chance that you’ll pass on the gene to each of your children.
Complications:
Complications depend on the types of signs and symptoms you have. For example, overly flexible joints can result in joint dislocations and early-onset arthritis. Fragile skin may develop prominent scarring.
People who have vascular Ehlers-Danlos syndrome are at risk of often fatal ruptures of major blood vessels. Some organs, such as the uterus and intestines, also may rupture. Pregnancy can increase the risk of a rupture in the uterus.
Prevention:
If you have a personal or family history of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome and you’re thinking about starting a family, you may benefit from talking to a genetic counselor — a health care professional trained to assess the risk of inherited disorders. Genetic counseling can help you understand the inheritance pattern of the type of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome that affects you and the risks it poses for your children.
Diagnosing Ehlers-Danlos syndrome:
Diagnosing rests on the criteria, physical examination, and quite often an extensive detailed family history by the M.D. Extremely loose joints, fragile or stretchy skin, and a family history of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome are often enough to make a diagnosis. Genetic tests on a sample of your blood can confirm the diagnosis in rarer forms of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome and help rule out other problems. For hypermobile Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, the most common form, there is no genetic testing available.
Treatments:
Unfortunately there is no cure for Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, but treatment can help you manage your symptoms and prevent further complications through the following:
Medications
Your doctor may prescribe drugs to help you control:
- Pain. Over-the-counter pain relievers — such as acetaminophen (Tylenol, others) ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) and naproxen sodium (Aleve) — are the mainstay of treatment. Stronger medications are only prescribed for acute injuries.
- Blood pressure. Because blood vessels are more fragile in some types of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, your doctor may want to reduce the stress on the vessels by keeping your blood pressure low.
Physical therapy
Joints with weak connective tissue are more likely to dislocate. Exercises to strengthen the muscles and stabilize joints are the primary treatment for Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. Your physical therapist might also recommend specific braces to help prevent joint dislocations.
Surgical and other procedures
Surgery may be recommended to repair joints damaged by repeated dislocations, or to repair ruptured areas in blood vessels and organs. However, the surgical wounds may not heal properly because the stitches may tear through the fragile tissues.
 each pt varies in intensity
each pt varies in intensity





