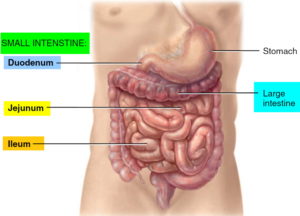
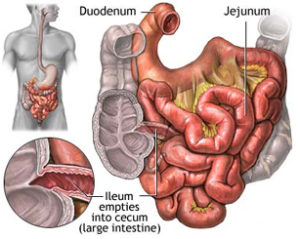
Intussusception is the most common cause of intestinal obstruction in children between ages 3 months and 3 years old. Intussusception occurs when a portion of the intestine folds like a telescope, with one segment slipping inside another segment. It can occur in the colon, the small bowel, or between the small bowel and colon. The result can be a blocked small bowel or colon. This causes an obstruction, preventing the passage of food that is being digested through the intestine.
Intussusception (in-tuh-suh-SEP-shun) is a serious condition in which part of the intestine slides into an adjacent part of the intestine.The walls of the 2 “telescoped” sections of intestine press on each other, causing irritation and swelling. Eventually, the blood supply to that area is cut off, which can cause damage to the intestine. This “telescoping” often blocks food or fluid from passing through. Intussusception also cuts off the blood supply to the part of the intestine that’s affected, which can lead to a tear in the bowel (perforation), infection and death of bowel tissue.
Intussusception is the most common cause of intestinal obstruction in children younger than 3. The cause of most cases of intussusception in children is unknown. Though rare in adults, most cases of adult intussusception are the result of an underlying medical condition, such as a tumor.
In children, the intestines can usually be pushed back into position with an X-ray procedure. In adults, surgery is often required to correct the problem.
Symptoms:
Children
The first sign of intussusception in an otherwise healthy infant may be sudden, loud crying caused by abdominal pain. Infants who have abdominal pain may pull their knees to their chests when they cry.
The pain of intussusception comes and goes, usually every 15 to 20 minutes at first. These painful episodes last longer and happen more often as time passes.
Other frequent signs and symptoms of intussusception include:
- Stool mixed with blood and mucus (sometimes referred to as “currant jelly” stool because of its appearance)
- Vomiting
- A lump in the abdomen
- Lethargy
- Diarrhea
- Fever
Not everyone has all of the symptoms. Some infants have no obvious pain, and some children don’t pass blood or have a lump in the abdomen. Some older children have pain but no other symptoms.
Adults
Because intussusception is rare in adults and symptoms of the disorder often overlap with the symptoms of other disorders, it’s more challenging to identify. The most common symptom is abdominal pain that comes and goes. Nausea and vomiting may also occur. People sometimes have symptoms for weeks before seeking medical attention.
When to see a doctor
Intussusception requires emergency medical care. If you or your child develops the signs or symptoms listed above, seek medical help right away.
In infants, remember that signs of abdominal pain may include recurrent bouts of pulling the knees to the chest and crying.
Causes:
Your intestine is shaped like a long tube. In intussusception, one part of your intestine — usually the small intestine — slides inside an adjacent part. This is sometimes called telescoping because it’s similar to the way a collapsible telescope folds together.
In some cases, the telescoping is caused by an abnormal growth in the intestine, such as a polyp or a tumor (called a lead point). The normal wave-like contractions of the intestine grab this lead point and pull it and the lining of the intestine into the bowel ahead of it. In most cases, however, no cause can be identified for intussusception.
Children
In the vast majority of cases of intussusception in children, the cause is unknown. Because intussusception seems to occur more often in the fall and winter and because many children with the problem also have flu-like symptoms, some suspect a virus may play a role in the condition. Sometimes, a lead point can be identified as the cause of the condition — most frequently the lead point is a Meckel’s diverticulum (a pouch in the lining of the small intestine).
Adults
In adults, intussusception is usually the result of a medical condition or procedure, including:
- A polyp or tumor
- Scar-like tissue in the intestine (adhesions)
- Weight-loss surgery (gastric bypass) or other surgery on the intestinal tract
- Inflammation due to diseases such as Crohn’s disease
Risk factors:
Risk factors for intussusception include:
- Age. Children — especially young children — are much more likely to develop intussusception than adults are. It’s the most common cause of bowel obstruction in children between the ages of 6 months and 3 years.
- Sex. Intussusception more often affects boys.
- Abnormal intestinal formation at birth. Intestinal malrotation is a condition in which the intestine doesn’t develop or rotate correctly, and it increases the risk for intussusception.
- A prior history of intussusception. Once you’ve had intussusception, you’re at increased risk of developing it again.
- A family history. Siblings of someone who’s had an intussusception are at a much higher risk of the disorder.
Complications:
Intussusception can cut off the blood supply to the affected portion of the intestine. If left untreated, lack of blood causes tissue of the intestinal wall to die. Tissue death can lead to a tear (perforation) in the intestinal wall, which can cause an infection of the lining of the abdominal cavity (peritonitis).
Peritonitis is a life-threatening condition that requires immediate medical attention. Signs and symptoms of peritonitis include:
- Abdominal pain
- Abdominal swelling
- Fever
Peritonitis may cause your child to go into shock. Signs and symptoms of shock include:
- Cool, clammy skin that may be pale or gray
- A weak and rapid pulse
- Abnormal breathing that may be either slow and shallow or very rapid
- Anxiety or agitation
- Profound listlessness
A child who is in shock may be conscious or unconscious. If you suspect your child is in shock, seek emergency medical care right away.

