Archive | April 2020
QUOTE FOR WEDNESDAY:
“You can become infected by coming into close contact (about 6 feet or twoarm lengths) with a person who has COVID-19. COVID-19 is primarily spreadfrom person to person.• You can become infected from respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs, sneezes, or talks.• You may also be able to get it by touching a surface or object that has the virus on it, and then by touching your mouth, nose, or eyes.”
” A number of environmental factors influence the spread of communicable diseases that are prone to cause epidemics. The most important of these are:
water supply
sanitation facilities
food
climate.
A lack of safe water, inadequate excreta disposal facilities, poor hygiene, poor living conditions and unsafe food can all cause diarrhoeal diseases. These diseases are a major cause of suffering and death in an emergency situation.”
WHO World Health Organization https://www.who.int/www.who.int
QUOTE FOR WEDNESDAY:
“Environmental Risk Factors factors that affect certain areas in US with highier count of COVID-19!”
“What you get is the initial damage and rush of inflammatory cells, but the damage is so extensive that the body’s immune response is completely overwhelmed — which causes even more immune response, more immune cells and more damage,” said Matthew Frieman, a virologist at the University of Maryland School of Medicine.
PMC U.S. National Library of Medicine/National Institutes of Health states, “Inflammation is a biological response of the immune system that can be triggered by a variety of factors, including pathogens, damaged cells and toxic compounds. These factors may induce acute and/or chronic inflammatory responses in the heart, pancreas, liver, kidney, lung, brain, intestinal tract and reproductive system, potentially leading to tissue damage or disease.
With infection, the virus probably begins to multiply inside cells lining the airway, which are fringed with hairlike structures. Coronaviruses that cause common colds are excellent at infecting the upper airway, while SARS tended to go deeper in the lungs. As the coronavirus gains strength, Frieman said, dead cells are sloughed off and collect in the airway, making breathing difficult.
Inflammation is the immune system’s response to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, toxic compounds, or irradiation [1], and acts by removing injurious stimuli and initiating the healing process [2]. Inflammation is therefore a defense mechanism that is vital to health [3]. Usually, during acute inflammatory responses, cellular and molecular events and interactions efficiently minimize impending injury or infection. This mitigation process contributes to restoration of tissue homeostasis and resolution of the acute inflammation. However, uncontrolled acute inflammation may become chronic, contributing to a variety of chronic inflammatory diseases [4].
At the tissue level, inflammation is characterized by redness, swelling, heat, pain, and loss of tissue function, which result from local immune, vascular and inflammatory cell responses to infection or injury [5]. Important microcirculatory events that occur during the inflammatory process include vascular permeability changes, leukocyte recruitment and accumulation, and inflammatory mediator release [2, 6].
Various pathogenic factors, such as infection, tissue injury, or cardiac infarction, can induce inflammation by causing tissue damage. The etiologies of inflammation can be infectious or non-infectious (Table (Table1).1). In response to tissue injury, the body initiates a chemical signaling cascade that stimulates responses aimed at healing affected tissues. These signals activate leukocyte chemotaxis from the general circulation to sites of damage. These activated leukocytes produce cytokines that induce inflammatory responses [7].
The inflammatory response is the coordinate activation of signaling pathways that regulate inflammatory mediator levels in resident tissue cells and inflammatory cells recruited from the blood [8]. Inflammation is a common pathogenesis of many chronic diseases, including cardiovascular and bowel diseases, diabetes, arthritis, and cancer [9]. Although inflammatory response processes depend on the precise nature of the initial stimulus and its location in the body, they all share a common mechanism, which can be summarized as follows: 1) cell surface pattern receptors recognize detrimental stimuli; 2) inflammatory pathways are activated; 3) inflammatory markers are released; and 4) inflammatory cells are recruited.”
This is why you see constant commercials stating to stay home especially if you have lung disease, diabetes, low immunity, and heart disease/high B/P. Including obesity. homeless, and the older age (60 years old and up). It’s like a car in that the longer you have the car the more wear and tear on the car well the same with the body for elderly and homeless. The older the patient the harder it is to fight the disease. So there are factors that involve bad turn outs for patients with Covid-19 virus that can go to lung damage to death.
Through worldometer.info as of this past Monday 976,176 cases of corona virus in the USA. Close to one million cases and where is the worst cases NY being in NYC and NJ (there next door neighbor). NY cases are 293,354 with total deaths 22,275
Through nyc.gov in NYC Total cases are 153,204, Hospitalized cases are 39, 635 Confirmed Deaths 11,460 Probable Deaths 5213
Through MSNBC/NBC/John’s Hopkins today at 1126 they show:
WORLDWIDE CASES OF CORONA CONFIRMED CASES: 2,989,493
Total America Confirmed Cases: 974,500
Worldwide with most confirmed cases:
United States: 974, 500 Spain: 226,629
Italy: 197, 675 France: 162, 220 Germany: 167, 770
Cases in America:
New York: 294, 491 New Jersey: 109, 038
Massachusetts: 54, 938 Illinois: 43, 903 California: 43, 672
(source of counts is John Hopkins/NBC NEWS April 27th 2020)
New York City: cases 153, 204 as of 4/26/2020 (Source is https://projects.thecity.nyc/2020 at 1708)
New York City: cases 158, 000 (Source from 2hrs ago by wikipedia, time 4/27/ 2020 is 1130)
Why is NYC over 1/2 the cases of America as of today at 1100?
Size of NYC – of the 5 bureau cities only covers 321 square miles, over 205,000 acres.
Population The population of people in NYC are 8.399 million not including illegals .
Dirtiest City in America – NYC
Sanctuary City – Leaders of sanctuary cities say they want to reduce fear of deportation and possible family break-up among people who are in the city illegally, this can definitely put a city at a potential risk for disease.
Low income groups in the city. This means that in New York City income of $68,720 for a family of four is considered to be low income. (https://www.povertycenter.columbia.edu/poverty-disadvantage-in-new-york-city)
About 1.7 million New Yorkers lived below the poverty line in 2011-2015. This number is larger than the population of Philadelphia or Phoenix, and would be the country’s 7th largest city if ranked separately. The overall poverty rate in New York City has remained relatively steady since 1980, hovering at around 20%.
Homes – primarily apartments and small.
Subways & Buses – a major way of transportation in NYC. Standing right next to each other.
Two international airports – J.F.K. and La Guardia. Traveling in and out of America all over the world including China. In Manhattan there’s China town as well.
Pollution in NYC – in 1oth place the worst pollution by Yahoo Finance (the 7 of the 9 before it where all in California).
See the pattern why NYC is highest with Covid19 virus?
There were numerous factors putting NYC at risk for where they are in count this past year of Covid19 unfortunately and hopefully both Governor Cuomo and Mayor Deblasio will follow what Governor Cuomo stated in the past year on MSNBC that we need to look at this disaster and learn from it to allow us to be better prepared for when this type of a disaster occurs again since NYS, NYC and of course other states were not. Governor Cuomo and facts on epidemics through historical literature points out examples of disasters Americans have gone through before from Great Chicago Fire, Depression, Spanish Flu, 2008 Flu and others which made our nation stronger.
QUOTE FOR TUESDAY:
“A widowmaker heart attack occurs when the left anterior descending (LAD) artery, which supplies blood to the larger, front part of the heart, is blocked at its origin. “This artery delivers a major amount of blood to your heart,” Dr. Abdallah explains.”
Cleveland Clinic
QUOTE FOR MONDAY:
“You can become infected by coming into close contact (about 6 feet or twoarm lengths) with a person who has COVID-19. COVID-19 is primarily spreadfrom person to person.• You can become infected from respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs, sneezes, or talks.• You may also be able to get it by touching a surface or object that has the virus on it, and then by touching your mouth, nose, or eyes.”
cdc.gov
QUOTES FOR THE WEEKEND:
Coronaviruses are composed of enveloped virions that contain a positive strand RNA genome. Human coronaviruses may cause the common cold or severe respiratory illness. In 2002 the SARS coronavirus emerged in China and spread globally, infecting over 8000 individuals and killing more than 900.
“On Tuesday, January 21, the Centers for Disease Control & Prevention (CDC) confirmed the first U.S. case of a coronavirus (2019 Novel Coronavirus, or 2019-nCoV) that originated last month in the central Chinese city of Wuhan. The patient had returned to Washington State last week from a trip to Wuhan, where 300 confirmed infections and several deaths have occurred. Thailand, Japan, and South Korea have also reported a handful of cases, all connected to travel from Wuhan. [January 24 update: A second U.S. case has been confirmed in Chicago, Illinois, and three cases have been confirmed in France.].
On January 30, the World Health Organization (WHO) Director-General declared that the 2019-nCoV outbreak constitutes a Public Health Emergency of International Concern.† On January 31, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) Secretary declared a U.S. public health emergency to respond to 2019-nCoV.§ Also on January 31, the president of the United States signed a “Proclamation on Suspension of Entry as Immigrants and Nonimmigrants of Persons who Pose a Risk of Transmitting 2019 Novel Coronavirus,” which limits entry into the United States of persons who traveled to mainland China to U.S. citizens and lawful permanent residents and their families.” USA Citizen Protection
CDC Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Reports suggest that 2019-nCoV was initially spread from animal-to-person. Currently, there are growing indications that there is limited person-to-person spread, though it is unclear how easily this may be happening.”
Hawaii.gov
QUOTE FOR FRIDAY:
“Both diseases may be treated with chemotherapy, radiation therapy and/or stem cell transplantation. Immunotherapy drugs may also help treat non-Hodgkin lymphoma and other hematological malignancies, such as multiple myeloma. “The early data suggests immunotherapy will play a future role in the management of lymphomas,” says Dr. Maurie Markman, President of Medicine and Science for Cancer Treatment Centers of America® (CTCA).”
Cancer Treatment Centers of America
QUOTE FOR THURSDAY:
“Lymphoma affects the body’s lymph system (also known as the lymphatic system). The lymph system is part of the immune system, which helps fight infections and some other diseases. It also helps fluids move through the body.”
American Cancer Society
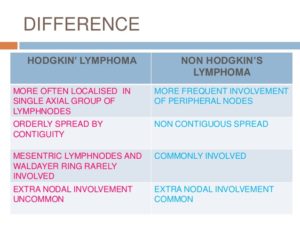
Hodgkin’s Lymphoma versus Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma

A particular cell known as the Reed-Sternberg cell is found in the biopsies. This cell is not usually found in other lymphomas, therefore they are called non Hodgkins lymphoma. This may not seem a very big difference, but it is important because the treatment for Hodgkins and non Hodgkins lymphomas can be very different.
Although the diseases may sound similar, there is a lot of difference between Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
Both Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphoma are malignancies of a family of white blood cells known as lymphocytes, which help the body fight off infections and other diseases.
Both Hodgkin’s lymphoma and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma are lymphomas — a type of cancer that begins in a subset of white blood cells and these are called lymphocytes. Lymphocytes are an integral part of your immune system, which protects you from germs.
The main difference between Hodgkin’s lymphoma and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma is in the specific lymphocyte each involves but also it includes:
| Hodgkin lymphoma | Non-Hodgkin lymphoma |
|---|---|
| Thirty-two percent of patients diagnosed with Hodgkin lymphoma are 20-34 years old. The median age of a patient diagnosed with the disease is 39. | Seventy-five percent of patients diagnosed with Hodgkin lymphoma 55 or older. The median age of a patient diagnosed with the disease is 66. |
| Hodgkin lymphoma is rare, accounting for about .5 percent of all new cancers diagnosed. An estimated 8,500 cases were diagnosed in 2016. | Non-Hodgkin lymphoma is the seventh most diagnosed cancer, accounting for an estimated 72,500 cases in 2016. |
| More than 86 percent of patients diagnosed with Hodgkin lymphoma survive five years or more. | About 70 percent of patients diagnosed with non-Hodgkin lymphoma survive five years or more. |
| There are six varieties of Hodgkin lymphoma. The most common forms are nodular sclerosis classical Hodgkin lymphoma and mixed cellularity classical Hodgkin lymphoma. They account for about 90 percent of all cases. | There are more than 61 types and subtypes of non-Hodgkin lymphoma. B-cell lymphomas account for 85 percent of all cases. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma is the most common form on non-Hodgkin lymphoma. |
Sources: National Cancer Institute and Lymphoma Research Foundation 2016
Hodgkin lymphoma is marked by the presence of Reed-Sternberg cells, which are mature B cells that have become malignant, are unusually large, and carry more than one nucleus. The first sign of the disease is often the appearance of enlarged lymph nodes. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma, by contrast, can be derived from B cells or T cells and can arise in the lymph nodes as well as other organs. (B cells and T cells play different roles in the body’s immune response to disease.)
In 2017 by the Mayo Clinic it states both diseases are relatively rare, but non-Hodgkin lymphoma is more common in the United States, with more than 70,000 new cases diagnosed each year, compared to about 8,000 for Hodgkin lymphoma. The median age of patients with non-Hodgkin lymphoma is 60, but it occurs in all age groups. Hodgkin lymphoma most often occurs in people ages 15 to 24 and in people over 60. There are more than 60 distinct types of non-Hodgkin lymphoma, whereas Hodgkin lymphoma is a more homogeneous disease.
The two forms of lymphoma are marked by a painless swelling of the lymph nodes. Hodgkin lymphomas are more likely to arise in the upper portion of the body (the neck, underarms, or chest). Non-Hodgkin lymphoma can arise in lymph nodes throughout the body, but can also arise in normal organs. Patients with either type can have symptoms such as weight loss, fevers, and night sweats.
The diseases often follow different courses of progression. Hodgkin lymphoma tends to progress in an orderly fashion, moving from one group of lymph nodes to the next, and is often diagnosed before it reaches an advanced stage. Most patients with non-Hodgkin lymphoma are diagnosed at a more advanced stage.
Treatments for lymphoma vary depending on the type of disease, its aggressiveness, and location, along with the age and general health of the patient. As a general rule, however, Hodgkin lymphoma is considered one of the most treatable cancers, with more than 90 percent of patients surviving more than five years. Survival rates for patients with non-Hodgkin lymphoma tend to be lower, but for certain types of the disease, the survival rates are similar to those of patients with Hodgkin lymphoma.
A doctor can tell the difference between Hodgkin’s lymphoma and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma by examining the cancer cells under a microscope. If in examining the cells, the doctor detects the presence of a specific type of abnormal cell called a Reed-Sternberg cell, the lymphoma is classified as Hodgkin’s. If the Reed-Sternberg cell is not present, the lymphoma is classified as non-Hodgkin’s.
Many subtypes of lymphoma exist, and your doctor will use laboratory tests to examine a sample of your lymphoma cells to determine your specific subtype. Expect to wait a few days to receive results from these specialized tests.
Your type of lymphoma helps your doctor determine your prognosis and your treatment options. The types of lymphoma have very different disease courses and treatment choices, so an accurate diagnosis is an integral part of getting the care you need.
How both Hodgkin’s and Non-Hodgkin’s Disease are diagnosed:
- Physical exam. Your doctor checks for swollen lymph nodes, including in your neck, underarm and groin, as well as for a swollen spleen or liver.
- Blood and urine tests. Blood and urine tests may help rule out an infection or other disease. A sample of your blood is examined in a lab to see if anything in your blood indicates the possibility of cancer (in both of these diseases particularly the WBCs).
- Imaging tests. Your doctor may recommend imaging tests to look for tumors in your body. Tests may include X-ray, CT, MRI and positron emission tomography (PET).
- Lymph node test. Your doctor may recommend a lymph node biopsy procedure to remove all or part of a lymph node for laboratory testing. Analyzing lymph node tissue in a lab may reveal whether you have non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma and, if so, which type. Your doctor may recommend a lymph node biopsy procedure to remove a lymph node for laboratory testing. He or she will diagnose classical Hodgkin’s lymphoma if abnormal cells called Reed-Sternberg cells are found within the lymph node.
- Bone marrow test. A bone marrow biopsy and aspiration procedure involves inserting a needle into your hipbone to remove a sample of bone marrow. The sample is analyzed to look for non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma cells to look for non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma cells or to look for non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma cells. This test is done on numerous types of cancer patients in helping to diagnose the cancer they have.