Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) have been known to mankind for centuries. Before the advent of modern medicine, people’s lack of awareness and understanding of STDs contributed to the widespread transmission of the infections while few or no treatments were available to treat the conditions.
In medieval times, syphilis and gonorrhoea were two of the most prevalent STDs in Europe.
Some STDs can have severe, life-changing consequences; syphilis, for example, can eventually cause progressive destruction of the brain and spinal cord, leading to mental dysfunction and hallucinations, speech problems and general paresis.
It’s kind of puzzling that sexually transmitted diseases are so prevalent—particularly when you consider that you have to get pretty up close and personal to contract one. An STD is characterized by any disease that is spread by one partner to another via sexual contact, and that can be orally, vaginally, anally, or via hand to genital contact. Regardless, they are spread when one partner passes the disease-causing organism on to the other. Obviously, preventing STD transmission is first and foremost by practicing safe sex (PREVENTION) and not enough do it in America for some crazy reason hurting themselves and other people. However, if you think you might have contracted one of the most common STDs, recognizing the disease is imperative for swift treatment and preventing further spreading.
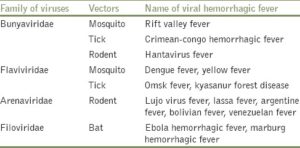
Top venereal diseases in the USA:
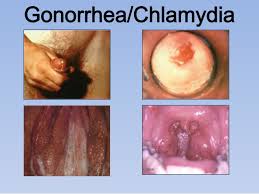
1-Gonorrhea
The Centers for Disease Control estimate that 700,000 new cases of Gonorrhea, or the “clap”, crop up every year. This long-term STD that is spread bacterially, affecting a female’s cervix, a male’s urethra, or the throat in both sexes, which means that it’s transmitted by vaginal, oral, and anal sex. The symptoms of gonorrhea are pretty subtle; the most noticeable being burning when urinating or a yellowish penile discharge in men.
2-Hepatitis
Sexually transmitted hepatitis is hepatitis B (or HBV), which afflicts more than 1.25 million individuals in the U.S. even though there is a vaccine. If left untreated, a Hep B infection will scar and damage the liver, causing cirrhosis and liver cancer. Unfortunately, over half of those affected show no symptoms, but those who do suffer muscle pain and fatigue, yellowing of the eyes (or jaundice), nausea, and a distended stomach.
3-Syphilis
Syphilis is a particularly sneaky STD that caused by a type bacterial infection of the genital tract, known as Treponema Pallidum. Syphilis is transmitted when direct contact is made between the small, painless sores on the mouth, rectum, vagina, or around the genitals in areas not protected by latex condoms. It can also be transmitted via infected mother to her baby during pregnancy. When there are no sores, the disease is still present. Syphilis symptoms are rare , however, the most telling are sores or lesions on and around the genitals, as well as hair loss, sore throat, fever; headache; and a white patchy skin rash.
4- Chlamydia
Like Gonorrhea, Chlamydia affects a man’s penile urethra and a woman’s cervix. However, oftentimes those who’ve contracted Chlamydia don’t show symptoms for months or even years, which explains why it’s the most common and rampant STD. If you do show symptoms, you’ll feel pain during intercourse and have a discolored, thick discharge from the vagina or penis. Transmitted via sexual penetration with an affected partner, using latex condoms can prevent transmission of this curable STD.
5. Crabs
If you feel a creepy-crawly, itchy sensation in your genitals, you may have crabs (or public lice). They show themselves as visible eggs or lice in the coarse hair of the genital region (even if you shave it off), and they can spread to the armpits and eyebrows if left untreated. Typically transmitted via sexual contact, crabs can also be passed via contact with infested linens or clothing .
6. Human Papilloma Virus
Human Papilloma Virus (or HPV) is currently the most wide spread STD. It affects roughly three-quarters of the sexually active population and a staggering one-quarter of sexually active women, which is why there is a North American vaccine to protect young women from certain types of HPV that are linked to genital warts and cervical cancer. HPV is transmitted through genital contact—via vaginal and anal sex, and also oral sex and genital-to-genital contact. Most times HPV doesn’t show any symptoms until it’s far advanced, but genital warts as well as RRP, a condition where warts grow in the throat and eventually cause breathing difficulties are common.
7. Bacterial Vaginosis
Bacterial Vaginosis, or BV, is not always considered an STD even though it typically afflicts those of child-bearing age with multiple or new sex partners. BV occurs when healthy bacteria in the vagina overgrow and become imbalanced, causing burning and itching around the vagina and a thick, grey discharge with a strong fishy odor. Antibiotics will quickly clear up bouts of BV, but it can reoccur, leaving the victim prone to pelvic inflammatory disease, other STDs, and premature births (if pregnant).
8. Herpes
Painful sores or lesions on your mouth or genitals may indicate herpes, a viral STD that comes in two forms HSV1 (herpes of the mouth) and HSV2 (herpes of the genitals). Herpes is transmitted skin-to-skin—for instance, from genital to genital, mouth to genital, or mouth to mouth contact with an infected individual, even when they don’t have visible sores. Even though herpes symptoms be treated with antibiotics, the virus never goes away and reoccurs typically 2 to 4 times per year.
9. Trichomoniasis
Trichomoniasis, or “trich”, often masks itself as a yeast infection or bacterial vaginosis (BV) in women with similar symptoms—including a thick, grey discharge, offensive vaginal odor, pain or burning intercourse, and itchiness. A parasitic trichomonas vaginalis infection affects the urethra and the vagina in women. It can be transmitted back and forth between sex partners (man to woman and woman to woman) via vaginal intercourse and contact. However, most men typically don’t have any symptoms.
10. HIV
HIV is transmitted via the exchange of body fluids—such as semen, vaginal secretions, blood, or breast milk. Within a month or 2 of contracting HIV, about 40 to 90-percent of those afflicted suffer from flu-like symptoms including fever, fatigue, achy muscles, swollen lymph glands, sore throat, headache, skin rash, dry cough, nausea, rapid weight loss, night sweats, frequent yeast infections (for women), cold sores, and eventually, pneumonia. Luckily, many individuals who are diagnosed early can live a long, productive life with HIV thanks to a combination of highly active anti-retroviral drug therapy, which prevents to progression to AIDS.
How you can prevent all these STDs are the following and its easy!
1.) Practice Abstinence 2.) Condoms 3.) The pill for women 4.) Fewer partners or one partner only and be checked prior to having sex through the doctor or clinic to make it safe for BOTH. 5.) Get Vaccinated.