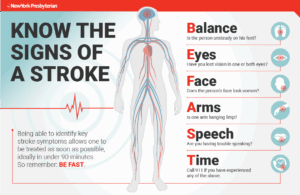
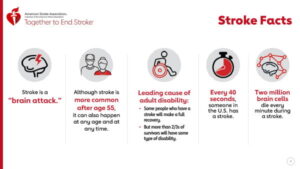
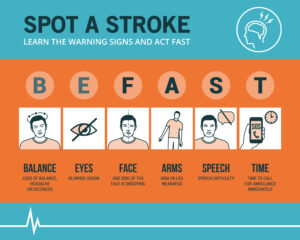

There are 2 types of strokes:
1-Hemmoragic-a blood vessel that bursts in the brain causing lack of oxygen to be supplied to the area of the brain (a lobe) where the vessel ruptured. Lack of oxygen to any area of the body tissue=starvation to the tissue; where in this case is the brain=a stroke.
2-Blockages-These blockages caused by the following: blood clots, athero-sclerosis, a common disorder, it happens due to fat, cholesterol, with even tar from smoking, or other substances that build up in the walls of the arteries forming hard structures called plaque and in time creating a blockage in the vessel interfering with blood supply providing oxygen to tissue and if blocked in the brain=high probability of a stroke occurring if not taken care of. “Recommended related to Heart Disease” by Web MD which states that atherosclerosis is the key cause of heart attacks & strokes including it’s the number one killer in the United States. Risk Factors for atherosclerosis include high blood pressure (b/p)=arteriosclerosis, blood level of high bad cholesterol (LDL), blood level of low good cholesterol (HDL), smoking, diabetes, and history of heart attacks in your nuclear family. Definitely a healthy diet, having exercise in your life, and your weight within the therapeutic body mass index level will help prevent, if not treat, atherosclerosis.
The Risk Factors of this disease, especially diet & sedentary lifestyle:
1. High Blood Pressure (b/p)-This is also known as the diagnosis hypertension. In understanding how hypertension works let’s use a metaphor: Think of a blood vessel as a long thin balloon and if we stand on it the pressure will increase inside the balloon causing the diameter of the balloon to swell up. If you continue to step on the balloon adding additional pressure this causes it to finally reach it’s total amount of pressure or when you exceed the total level of pressure this results in popping the balloon. Similar concept with high b/p, that’s if the pressure keeps rising in our blood vessels due to blockage or vasoconstriction (which is making the vessels diameter more narrow=increased pressure in the vessels) sooner or later a vessel bursts somewhere in the body due to the b/p passing it’s total level in the amount of pressure that it can handle in the circulatory system which can result into a burst of an artery, like in the brain causing a stroke or in a vessel near the heart causing a myocardial infarction (but this is another topic some other day). Think of food, a human being not eating leads into starvation, well for blood cells lack of oxygen=starvation to the cells. This causes in both situations or cases a lack of nutrition (the tissue is lacking oxygen). With a stroke, not enough oxygen is getting to the brain resulting from either a hemorrhage (loosing too much blood=loosing to many cells=oxygen (food for tissue) or a blockage preventing 02 getting to the area. Though many people have increased b/p due to only 2 things diet leading them to obesity, and lack of exercise due to a sedentary lifestyle, which could be changed and resolve the problem in most cases. Increased b/p can also be due noncompliance- like continuing to smoke, or not following the healthy regimen the M.D. ordered for you as a patient. The overall healthy regimen for a person with hypertension would be a low sodium diet (preventing further vasoconstriction), even low in cholesterol/fat/1800-2000 calories a day (preventing obesity or further weight gain), balancing rest with exercise and the b/p medications taken as prescribed, by their M.D. So for many Americans hypertension can be controlled just by diet with balancing exercise with rest. For others it might take a little more like doing which is what I just mentioned with following your medication regimen as ordered and going to your doctor having your b/p monitored, as your M.D. prescribes. 2. Smoking-For starters, this unhealthy habit puts you at risk for high blood pressure since it causes vasoconstriction (narrowing) of the vessels in our body due to the nicotine. The answer to this risk factor is simply quit this unhealthy habit. Smoking adds to the plaque building up in the vessels. Centers for Disease state that in 2010 the leading cause of death was heart disease followed by cancer than to chronic respiratory disease and lastly stroke. Over time a healthy diet balanced with exercise daily or every 2 days for 30minutes would help decrease the cardiac disease and stroke. The American Lung Association states that smoking is directly responsible for approximately 90 percent of lung cancer deaths and approximately 80-90 percent of COPD (emphysema and chronic bronchitis) deaths.
- Among adults who have ever smoked, 70% started smoking regularly at age 18 or younger, and 86% at age 21 or younger.3
- Smoking harms nearly every organ in the body, and is a main cause of lung cancer and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD, including chronic bronchitis and emphysema). It is also a cause of coronary heart disease (CAD), stroke and a host of other cancers and diseases.
So let’s take a car for instance, if the transmission is bad and not repaired by a mechanic the engine will be effected and soon fail completely. Now let’s take the lungs, if they are bad and you don’t go to a doctor to help treat the problem the heart will be effected at some point to failure in function and vice versa. If a smoker doesn’t quit it causes COPD=Emphysema (this does take over years) and it will affect the heart in time to not function as effectively with someone who has healthy lungs. Worse, if you don’t quit smoking you increase the risk of getting CAD (coronary artery disease) and add to the problem atherosclerosis if you already have the diagnosis which is caused by fatty materials (lipids), fibrous tissue with tar (from the smoking) causing blockages in the vessels. You also have a risk at lung cancer.
3. High Cholesterol-The National Stroke Association states the following about cholesterol:
Cholesterol is a soft, waxy fat (lipid) that is made by the body. It is found in the bloodstream and in all of your body’s cells. The body needs cholesterol to form cell membranes, some hormones and vitamin D.
Cholesterol is also found in some foods, such as seafood, eggs, meats and dairy products.
Because cholesterol does not dissolve in the blood on its own, it must be carried to and from cells by particles called lipoproteins. There are two main types of lipoproteins: low-density lipoproteins (LDL)=the bad cholesterol and high-density lipoproteins=the good cholesterol (HDL).
LDL can cause plaque build-up. Plaque is a thick, hard substance that can clog arteries. Recent studies show that high levels of LDL and triglycerides (blood fats) raise the risk of ischemic stroke. Plaque can also increase risk of a transient ischemic attack (TIA) where stroke symptoms go away within 24 hours. Stroke verses TIA=Nonreversible verses Reversible. Stroke is scarring to the brain where TIA doesn’t. Like Heart Attack verses Angina, Heart Attack is scarring to the heart verses no scarring to the heart with Angina. Both Angina and TIA are just lack of oxygen to the heart and the brain, causing the symptoms due to lack of oxygen=ischemia. Both heart attack and stroke are both a lot worse than just ischemia. They both get to the point where there in no oxygen causing actual permanent damage to the organ since the problem never reversed=scarring to the heart and brain.
The second main type of cholesterol is high-density lipoprotein (HDL), often called the “good” cholesterol. High levels of HDL may reduce stroke risk.
High cholesterol levels or plaque build-up in the arteries can block normal blood flow to the brain and cause a stroke. High cholesterol may also increase the risk of heart disease and atherosclerosis, which are both risk factors for stroke.
Many things can affect the b/p levels & cholesterol levels. Some can be changed and some cannot. We can change 3 things. You can change, anyone can change, it’s up to you in deciding whether to do it or not and being able to discipline yourself with having the power to do it. They are:
1-Diet — Foods high in saturated fat and cholesterol can increase cholesterol levels.
2-Weight — Being overweight can increase your cholesterol levels.
3-Exercise — People who are not active tend to have higher cholesterol levels.
These 3 things can prone you to high blood pressure (B/P), a stroke, & cardiac disease and even other diseases. I just had a dear friend who I’ve known almost 35 years that survived coronary artery bypass surgery over 55 y/o, with 5 blockages (2 100% blocked and 3 at least 80% blocked). That was a set up for a silent heart attack if he didn’t have the surgery but he was lucky in getting symptoms of chest pain and fatigue/lethargy due to these blockages. This made him go the doctor. He stopped smoking the day before the surgery. His life had taken a 360 turn and stopped in his daily routine and life schedule. It had begin all over again at almost 60.
Without controlling your blood pressure therapeutically or ending your smoking or eating healthy with living healthy habits the heart at first will be able to compensate with living unhealthy habits but over time the heart may find it so hard to function or work that the heart starts to fail in doing its job effectively (it decompensates causing failure if no changes are made). Again let’s take the car, you do maintenance to the vehicle it will operate and last longer, well the exact principle with the human body. Pretty simple isn’t it.
If you don’t eat a healthy diet, keep your weight in a therapeutic range, properly exercise than expect a high odds they will be leaning more towards a shortening of your life span. You can control your diet, weight and your exercise the right way with a little direction. We are here for just direction in helping you maintain a good diet including weight and giving you guidance. Healthy habits in giving you knowledge about routine exercise, all 4 food groups and how to eat them in healthy proportions are the important key.
It is all up to you in making the choice on your life where you can make it more enjoyable and less restricted now and at retirement by sticking to a good health diet and healthy habits, not for 3 or 6 months but for life. You make all the decisions in what you want to do with your body with what’s acceptable.