If you have been reading regularly on this blog than you know this day is dedicated everywhere for the health topic “WORLD HEART DAY”.
Governments and non-government organizations celebrate and promote World Heart Day with activities such as fun runs, public talks, concerts, and sporting events. The World Heart Federation organizes awareness events in more than 100 countries. They include:
- Health checks.
- Sports events, including walks, runs and fitness sessions.
- Public talks and science forums
- Stage shows and concerts.
- Exhibitions.
The World Heart Foundation organizes World Heart Day, an international campaign held on September 29 to inform people about cardiovascular diseases.
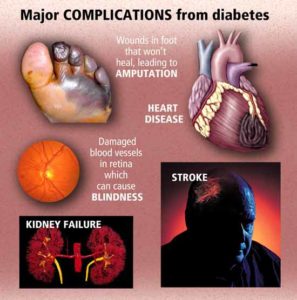
Cardiovascular Diseases:
Coronary heart disease is a common term for the buildup of plaque in the heart’s arteries that could lead to heart attack. But what about coronary artery disease? Is there a difference?
The short answer is often no — health professionals frequently use the terms interchangeably.
However, coronary heart disease , or CHD, is actually a result of coronary artery disease, or CAD, said Edward A. Fisher, M.D., Ph.D., M.P.H., an American Heart Association volunteer who is the Leon H. Charney Professor of Cardiovascular Medicine and also of the Marc and Ruti Bell Vascular Biology and Disease Program at the NYU School of Medicine.
Coronary heart disease is a common term for the buildup of plaque in the heart’s arteries that could lead to heart attack. But what about coronary artery disease? Is there a difference?
The short answer is often no — health professionals frequently use the terms interchangeably.
However, coronary heart disease , or CHD, is actually a result of coronary artery disease, or CAD, said Edward A. Fisher, M.D., Ph.D., M.P.H., an American Heart Association volunteer who is the Leon H. Charney Professor of Cardiovascular Medicine and also of the Marc and Ruti Bell Vascular Biology and Disease Program at the NYU School of Medicine.
With coronary artery disease, plaque first grows within the walls of the coronary arteries until the blood flow to the heart’s muscle is limited. View an illustration of coronary arteries. This is also called ischemia. It may be chronic, narrowing of the coronary artery over time and limiting of the blood supply to part of the muscle. Or it can be acute, resulting from a sudden rupture of a plaque and formation of a thrombus or blood clot.
The traditional risk factors for coronary artery disease are high LDL cholesterol, low HDL cholesterol, high blood pressure, family history, diabetes, smoking, being post-menopausal for women and being older than 45 for men, according to Fisher. Obesity may also be a risk factor.
“Coronary artery disease begins in childhood, so that by the teenage years, there is evidence that plaques that will stay with us for life are formed in most people,” said Fisher, who is former editor of the American Heart Association journal, ATVB. “Preventive measures instituted early are thought to have greater lifetime benefits. Healthy lifestyles will delay the progression of CAD, and there is hope that CAD can be regressed before it causes CHD.”
Living a healthy lifestyle that incorporates good nutrition, weight management and getting plenty of physical activity can play a big role in avoiding CAD.
“Coronary artery disease is preventable,” agreed Johnny Lee, M.D., president of New York Heart Associates, and an American Heart Association volunteer. “Typical warning signs are chest pain, shortness of breath, palpitations and even fatigue.”
What is a “widow maker”? Well for starters, this is the deadliest heart attack. The symptoms you need to know to possibly prevent the results of this widow maker. It occurs when there is a complete blockage of the left artery feeding the heart with blood. This causes a cut off of oxygen supply to one of the large parts of the heart muscle, which can cause it to stop beating, causing you to die.
A heart attack is when one of the coronary arteries becomes blocked.
The heart muscle is then robbed of vital oxygenated blood, which if left untreated, can cause the heart muscle to begin to die.
A heart attack is a life-threatening emergency.
A widow maker heart attack is caused when the LAD artery becomes blocked.
It occurs when there’s a complete blockage of the left anterior descending (LAD) artery, one of two main arteries that brings OXYGENATED blood to the heart=FOOD TO THE HEART MUSCLE (O2).
When it is blocked due to a build up of plaque it is most often deadly, hence the name “widow maker”. How to we get plaque build up?
Cholesterol plaques can be the cause of heart disease. Plaques begin in artery walls and grow over years. The growth of cholesterol! The plaques slowly blocks blood flow in the arteries. Worse, a cholesterol plaque can suddenly rupture. The sudden blood clot that forms over the rupture then causes a heart attack or stroke.
Blocked arteries caused by plaque buildup and blood clots are the leading cause of death in the U.S. Reducing cholesterol and other risk factors can help prevent cholesterol plaques from forming. Occasionally, it can even reverse some plaque buildup.
“When the main artery down the front of the heart (LAD) is totally blocked or has a critical blockage, right at the beginning of the vessel, it is known as the Widow Maker. (The medical term for this is a proximal LAD lesion). No one knows exactly who came up with the term, but the reason they did is likely that if that artery is blocked right at the beginning of its course, then the whole artery after it goes down. This essentially means that the whole front wall of the heart goes down. As far as heart attacks go, this is a big one, with big consequences if not dealt with appropriately and FAST!”
myheart.net/Dr. Ahmed – an Interventional Cardiologist and Director of Structural Heart Disease at Princeton-Baptist Hospital.
Symptoms:
A widow maker heart attack has the same symptoms as any other heart attack.
They can be difficult to spot for sure, because they can vary from person to person.
The most common signs include:
- chest pain, tightness, heaviness, pain or a burning feeling in your chest
- pain in the arms, neck, jaw, back or stomach
- for some people the pain and tightness will be severe, while for others it will just feel uncomfortable
- sweating
- feeling light-headed
- becoming short of breath
- feeling nauseous or vomiting
How is a heart attack treated?
The first port of call for treatment, is for doctors to treat the blocked artery.
There are two main procedures used to open up the blocked blood vessel.
The first, a primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PPCI) is an emergency coronary angioplasty.
It opens the blockage and helps restore blood supply to the heart.
The second treatment, is thrombosis, also known as a “clot buster”.
It involves injecting a drug into the vein to dissolve the blood clot and restore blood supply to the heart that way. In some cases this procedure can be performed in the ambulance.
While these treatments are common, in some cases they will not be right for the patient and so won’t be performed. The MD Cardiologist will know the right Rx.
Take good care of your HEART, the engine to the human body! First do all preventative measures to prevent getting any cardiovascular diseases but if you have cardiovascular diseases then follow your M.D. instructions on any meds if he prescribed them for you, eat the proper foods for a cardiac diet, and balance rest with exercise. See your cardiologist as he or she recommends.

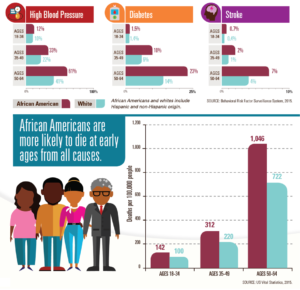 KEEPING IN MIND:
KEEPING IN MIND: