Short review of what is cystic fibrosis?
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a genetic disease. This means that CF is inherited.
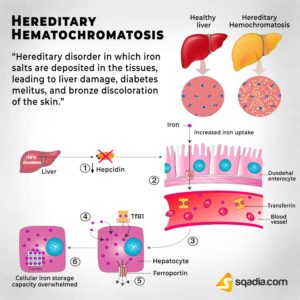
Mutations in a gene called the CFTR (cystic fibrosis conductance transmembrane regulator) gene cause CF. The CFTR mutations causes changes in the body’s cell’s electrolyte transport system. Electrolytes are substances in blood that are critical to cell function. The main result of these transport system changes are seen in the body secretions, such as mucus and sweat.
The CFTR gene is quite large and complex. There are many different mutations in this gene that have been linked to CF.
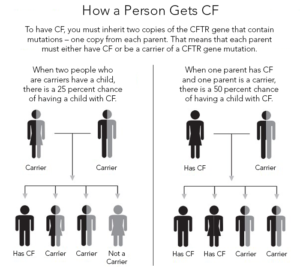
A person will be born with CF only if 2 CF genes are inherited–one from the mother and one from the father. An individual must inherit two non-functioning CF genes – one from each parent – to have CF. If both parents are carriers there is a 1 in 4 (25 percent) chance that both will pass on the non-functioning gene, which would result in a pregnancy affected with cystic fibrosis.
A person who has only one CF gene is called a CF carrier. They are healthy and don’t have the disease. But they are a carrier of the disease. See above box in specifics how much a infant is at risk getting the disease.
CF affects various organ systems in children and young adults, including the following:
- Respiratory system
- Digestive system
- Reproductive system
How does CF affect the respiratory system?
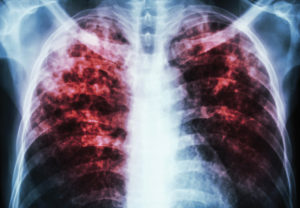
The abnormal electrolyte transport system in CF causes the cells in the respiratory system, especially the lungs, to absorb too much sodium and water. This causes the normal thin secretions in the lungs to become very thick and hard to move. These thick secretions increase the risk for frequent respiratory infections.
Recurrent respiratory infections lead to progressive damage in the lungs, and eventually death of the cells in the lungs.
Because of the high rate of infection in the lower respiratory tract, people with CF may develop a chronic cough, blood in the sputum, and often even have a collapsed lung. The cough is usually worse in the morning or after activity.
People with CF also have upper respiratory tract symptoms. Some have nasal polyps that need surgical removal. Nasal polyps are small protrusions of tissue from the lining of the nose that can block and irritate the nasal cavity. People with CF also have higher rates of sinus infections.
How does CF affect the gastrointestinal (GI) system?
CF mainly affects the pancreas. The pancreas secretes substances that aid digestion and help control blood sugar levels.
The secretions from the pancreas also become thick and can clog the ducts of the pancreas. This may cause a decrease in the secretion of enzymes from the pancreas that normally help digest food. A person with CF has trouble absorbing proteins, fats, and vitamins A, D, E, and K.
The problems with the pancreas can become so severe that some of the cells in the pancreas die. Over time, this may lead to glucose intolerance and Cystic Fibrosis-Related Diabetes (CFRD), a unique type of insulin-dependent diabetes.
The symptoms of CF that may be due to involvement with the GI tract include:
- Bulky, greasy stools
- Rectal prolapse (a condition in which the lower end of the bowel comes out of the anus)
- Delayed puberty
- Fat in the stools
- Stomach pain
- Bloody diarrhea
The liver may also be affected. A small number of people may develop liver disease. Symptoms of liver disease include:
- Enlarged liver
- Swollen belly
- Yellow color to the skin (jaundice)
- Vomiting of blood
How does CF affect the reproductive system?
Most males with CF have blockage of the sperm canal. This is called congenital bilateral absence of the vas deferens (CBAVD). This results from the thick secretions clogging the vas deferens and keeping them from developing properly. It causes infertility because sperm can’t travel out of the body. There are some newer techniques that allow men with cystic fibrosis to have children. These should be discussed with your healthcare provider. Women also have an increase in thick cervical mucus that may lead to a decrease in fertility, although many women with CF are able to have children.
Who is at risk for cystic fibrosis?
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is inherited, and a person with CF had both parents pass the altered gene to them. The birth of a child with CF is often a total surprise to a family, since most of the time there is no family history of CF.
Symptoms can include with above symptoms the following:
All U.S. states require that newborns be tested for cystic fibrosis (CF). This means that parents can know if their baby has the disease and can take precautions and watch for early signs of problems.
The following are the most common symptoms of CF. However, people may experience symptoms differently, and the severity of symptoms can vary, too. Symptoms may include:
- Thick mucus that clogs certain organs, such as the lungs, pancreas, and intestines. This may cause malnutrition, poor growth, frequent respiratory infections, breathing problems, and chronic lung disease.
Many other medical problems can point to cystic fibrosis, as well. These include:
Sinusitis, Nasal polyps, Clubbing of fingers and toes. This means thickened fingertips and toes because of less oxygen in the blood, Collapse of the lung often due to intense coughing, Coughing up blood, Enlargement of the right side of the heart due to increased pressure in the lungs (Cor pulmonale), Abdominal pain, Excess gas in the intestines, Rectal prolapse. In this condition, the lower end of the bowel comes out of the anus, Liver disease, Diabetes, Pancreatitis, or inflammation of the pancreas that causes severe pain in the belly, Gallstones, Congenital bilateral absence of the vas deferens (CBAVD) in males. This causes blockages of the sperm canal.
The symptoms of CF differ for each person.
Infants born with CF usually show symptoms by age 2. Some children, though, may not show symptoms until later in life. The following signs are suspicious of CF, and infants having these signs may be further tested for CF:
Diarrhea that does not go away, Foul-smelling stools, Greasy stools, Frequent wheezing, Frequent pneumonia or other lung infections, Persistent cough, Skin that tastes like salt, Poor growth despite having a good appetite.
The symptoms of CF may resemble other conditions or medical problems. See a healthcare provider for a diagnosis.