Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism (under-active thyroid) is a condition that occurs when your thyroid produces too little thyroid hormone, a condition that is often linked to iodine deficiency.
Dr. David Brownstein, a board-certified holistic practitioner who has been working with iodine for the last two decades, claims that over 95 percent of the patients in his clinic are iodine-deficient.
In addition, 10 percent of the general population in the United States, and 20 percent of women over age 60, have subclinical hypothyroidism, a condition where you have no obvious symptoms and only slightly abnormal lab tests.
However, only a marginal percentage of these people are being treated. The reason behind this is the misinterpretation and misunderstanding of lab tests, particularly TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone). Most physicians believe that if your TSH value is within the “normal” range, your thyroid is fine. But as I always say, the devil is in the details. More and more physicians are now discovering that the TSH value is grossly unreliable for diagnosing hypothyroidism.
Hypothyroidism can cause a variety of signs and symptoms:
The most sensitive way to find out is to listen to your body. People with a sluggish thyroid usually experience:
Lethargy – Fatigue and lack of energy are typical signs of thyroid dysfunction. Depression has also been linked to the condition. If you’ve been diagnosed with depression, make it a point that your physician checks your thyroid levels.
-
- It’s essential to note that not all tiredness or lack of energy can be blamed on a dysfunctional thyroid gland. Thyroid-related fatigue begins to appear when you cannot sustain energy long enough, especially when compared to a past level of fitness or ability. If your thyroid foundation is weak, sustaining energy output is going to be a challenge. You will notice you just don’t seem to have the energy to do the things like you used to.
-
-
- Feeling like you don’t have the energy to exercise, and typically not exercising on a consistent basis
- A heavy or tired head, especially in the afternoon; your head is a very sensitive indicator of thyroid hormone status
- Falling asleep as soon as you sit down when you don’t have anything to do.
-
- Rough and scaly skin and/or dry, coarse, and tangled hair– If you have perpetually dry skin that doesn’t respond well to moisturizing lotions or creams, consider hypothyroidism as a factor.
- Hair loss– Women especially would want to pay attention to their thyroid when unexplained hair loss occurs. Fortunately, if your hair loss is due to low thyroid function, your hair will come back quickly with proper thyroid treatment.
- Sensitivity to cold– Feeling cold all the time is also a sign of low thyroid function. Hypothyroid people are slow to warm up, even in a sauna, and don’t sweat with mild exercise.
- Low basal temperature – Another telltale sign of hypothyroidism is a low basal body temperature (BBT), less than 97.6 degrees Fahrenheit averaged over a minimum of three days. It is best to get a BBT thermometer to assess this.
- Weight gain– Easy weight gain or difficulty losing weight, despite an aggressive exercise program and watchful eating, is another indicator.
Hypothyroidism in infants
Anyone can get hypothyroidism, including infants. Most babies born without a thyroid gland or with a gland that doesn’t work correctly don’t have symptoms right away. But if hypothyroidism isn’t diagnosed and treated, symptoms start to appear. They may include:
- Feeding problems.
- Poor growth.
- Poor weight gain.
- Yellowing of the skin and the whites of the eyes, a condition called jaundice.
- Constipation.
- Poor muscle tone.
- Dry skin.
- Hoarse crying.
- Enlarged tongue.
- A soft swelling or bulge near the belly button, a condition called umbilical hernia.
When hypothyroidism in infants isn’t treated, even mild cases can lead to severe physical and mental development problems.
Hypothyroidism in children and teens
In general, children and teens with hypothyroidism have symptoms similar to those in adults. But they also may have:
- Poor growth that leads to short stature.
- Delayed development of permanent teeth.
- Delayed puberty.
- Poor mental development.
When to see a doctor
See your health care provider if you’re feeling tired for no reason or if you have other symptoms of hypothyroidism.
If you’re taking thyroid hormone medicine for hypothyroidism, follow your health care provider’s advice on how often you need medical appointments. At first, you may need regular appointments to make sure you’re receiving the right dose of medicine. Over time, you may need checkups so that your health care provider can monitor your condition and medicine.
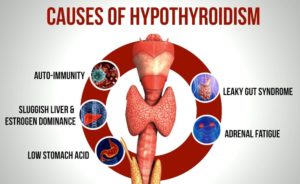
Causes:
The thyroid is a small, butterfly-shaped gland located at the base of the neck, just below the Adam’s apple. The thyroid gland makes two main hormones: thyroxine (T-4) and triiodothyronine (T-3). These hormones affect every cell in the body. They support the rate at which the body uses fats and carbohydrates. They help control body temperature. They have an effect on heart rate. And they help control how much protein the body makes.
Hypothyroidism happens when the thyroid gland doesn’t make enough hormones. Conditions or problems that can lead to hypothyroidism include:
- Autoimmune disease. The most common cause of hypothyroidism is an autoimmune disease called Hashimoto’s disease. Autoimmune diseases happen when the immune system makes antibodies that attack healthy tissues. Sometimes that process involves the thyroid gland and affects its ability to make hormones.
- Thyroid surgery. Surgery to remove all or part of the thyroid gland can lower the gland’s ability to make thyroid hormones or stop it completely.
- Radiation therapy. Radiation used to treat cancers of the head and neck can affect the thyroid gland and lead to hypothyroidism.
- Thyroiditis. Thyroiditis happens when the thyroid gland becomes inflamed. This may be due to an infection. Or it can result from an autoimmune disorder or another medical condition affecting the thyroid. Thyroiditis can trigger the thyroid to release all of its stored thyroid hormone at once. That causes a spike in thyroid activity, a condition called hyperthyroidism. Afterward, the thyroid becomes underactive.
- Medicine. A number of medicines may lead to hypothyroidism. One such medicine is lithium, which is used to treat some psychiatric disorders. If you’re taking medicine, ask your heath care provider about its effect on the thyroid gland.
Less often, hypothyroidism may be caused by:
- Problems present at birth. Some babies are born with a thyroid gland that doesn’t work correctly. Others are born with no thyroid gland. In most cases, the reason the thyroid gland didn’t develop properly is not clear. But some children have an inherited form of a thyroid disorder. Often, infants born with hypothyroidism don’t have noticeable symptoms at first. That’s one reason why most states require newborn thyroid screening.
- Pituitary disorder. A relatively rare cause of hypothyroidism is the failure of the pituitary gland to make enough thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). This is usually because of a noncancerous tumor of the pituitary gland.
- Pregnancy. Some people develop hypothyroidism during or after pregnancy. If hypothyroidism happens during pregnancy and isn’t treated, it raises the risk of pregnancy loss, premature delivery and preeclampsia. Preeclampsia causes a significant rise in blood pressure during the last three months of pregnancy. Hypothyroidism also can seriously affect the developing fetus.
- Not enough iodine. The thyroid gland needs the mineral iodine to make thyroid hormones. Iodine is found mainly in seafood, seaweed, plants grown in iodine-rich soil and iodized salt. Too little iodine can lead to hypothyroidism. Too much iodine can make hypothyroidism worse in people who already have the condition. In some parts of the world, it’s common for people not to get enough iodine in their diets. The addition of iodine to table salt has almost eliminated this problem in the United States.
Diseases caused by hypothyroidism include:
- Hashimoto’s disease (autoimmune disorder)
- Graves disease (autoimmune disorder)
- Iodine deficiency
- Congenital hypothyroidism (present at birth)
- Thyroiditis (inflammation of the thyroid)
- Surgical removal of part or all of the thyroid
When to be checked by the doctor:
When any of these signs or symptoms listed above if you have that where never checked out by the doctor or if the new symptom (s) just recently started that match the symptoms above and where never diagnosed by the MD . If you’ve been treated for hypothyroidism or even currently being treated, see your doctor regularly as advised so that he or she can monitor your condition. Also, if you are at a age that makes you in a age group that is more common to have this disease than have your MD check you out to see if you have the disease.
If hypothyroidism isn’t treated, it can cause some major health problems.
Risk factors
Although anyone can develop hypothyroidism, you’re at an increased risk if you:
- Are a woman.
- Have a family history of thyroid disease.
- Have an autoimmune disease, such as type 1 diabetes or celiac disease.
- Have received treatment for hyperthyroidism.
- Received radiation to your neck or upper chest.
- Have had thyroid surgery.
Complications
Hypothyroidism that isn’t treated can lead to other health problems, including:
- Goiter. Hypothyroidism may cause the thyroid gland to become larger. This condition is called a goiter. A large goiter may cause problems with swallowing or breathing.
- Heart problems. Hypothyroidism can lead to a higher risk of heart disease and heart failure. That’s mainly because people with an underactive thyroid tend to develop high levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol — the “bad” cholesterol.
- Peripheral neuropathy. Hypothyroidism that goes without treatment for a long time can damage the peripheral nerves. These are the nerves that carry information from the brain and spinal cord to the rest of the body. Peripheral neuropathy may cause pain, numbness and tingling in the arms and legs.
- Infertility. Low levels of thyroid hormone can interfere with ovulation, which can limit fertility. Some of the causes of hypothyroidism, such as autoimmune disorders, also can harm fertility.
- Birth defects. Babies born to people with untreated thyroid disease may have a higher risk of birth defects compared with babies born to mothers who do not have thyroid disease.Infants with hypothyroidism present at birth that goes untreated are at risk of serious physical and mental development problems. But if the condition is diagnosed within the first few months of life, the chances of typical development are excellent.
- Myxedema coma. This rare, life-threatening condition can happen when hypothyroidism goes without treatment for a long time. A myxedema coma may be triggered by sedatives, infection or other stress on the body. Its symptoms include intense cold intolerance and drowsiness, followed by an extreme lack of energy and then unconsciousness. Myxedema coma requires emergency medical treatment.