Causes
Liver disease has many causes.
Infection
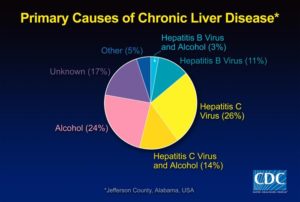
Parasites and viruses can infect the liver, causing inflammation that reduces liver function. The viruses that cause liver damage can be spread through blood or semen, contaminated food or water, or close contact with a person who is infected. The most common types of liver infection are hepatitis viruses, including:
- Hepatitis A
- Hepatitis B
- Hepatitis C
Immune system abnormality
Diseases in which your immune system attacks certain parts of your body (autoimmune) can affect your liver. Examples of autoimmune liver diseases include:
- Autoimmune hepatitis
- Primary biliary cirrhosis
- Primary sclerosing cholangitis
Genetics
An abnormal gene inherited from one or both of your parents can cause various substances to build up in your liver, resulting in liver damage. Genetic liver diseases include:
- Hemochromatosis
- Hyperoxaluria and oxalosis
- Wilson’s disease
- Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency
Cancer and other growths
Examples include:
- Liver cancer
- Bile duct cancer
- Liver adenoma
Other
Additional, common causes of liver disease include:
- Chronic alcohol abuse
- Fat accumulating in the liver (nonalcoholic fatty liver disease)
Risk factors
Factors that may increase your risk of liver disease include:
- Heavy alcohol use
- Injecting drugs using shared needles
- Tattoos or body piercings
- Blood transfusion before 1992
- Exposure to other people’s blood and body fluids
- Unprotected sex
- Exposure to certain chemicals or toxins
- Diabetes
- Obesity
Complications
Complications of liver disease vary, depending on the cause of your liver problems. Untreated liver disease may progress to liver failure, a life-threatening condition.
Prevention
To prevent liver disease:
- Drink alcohol in moderation. For healthy adults, that means up to one drink a day for women and up to two drinks a day for men. Heavy or high-risk drinking is defined as more than eight drinks a week for women and more than 15 drinks a week for men.
- Avoid risky behavior. Get help if you use illicit intravenous drugs, and don’t share needles used to inject drugs. Use a condom during sex. If you choose to have tattoos or body piercings, be picky about cleanliness and safety when selecting a shop.
- Get vaccinated. If you’re at increased risk of contracting hepatitis or if you’ve already been infected with any form of the hepatitis virus, talk to your doctor about getting the hepatitis A and hepatitis B vaccines.
- Use medications wisely. Take prescription and nonprescription drugs only when needed and only in recommended doses. Don’t mix medications and alcohol. Talk to your doctor before mixing herbal supplements or prescription or nonprescription drugs.
- Avoid contact with other people’s blood and body fluids. Hepatitis viruses can be spread by accidental needle sticks or improper cleanup of blood or body fluids.
- Take care with aerosol sprays. Make sure the room is ventilated, and wear a mask when spraying insecticides, fungicides, paint and other toxic chemicals. Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Protect your skin. When using insecticides and other toxic chemicals, wear gloves, long sleeves, a hat and a mask.
- Maintain a healthy weight. Obesity can cause nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.