Chronic Renal or Kidney Disease (CRF):
In giving a short and easily understandable definition Chronic kidney disease happens when your kidneys no longer filter your blood the way they should, so wastes (toxins, usually end products of an acid) build up in your blood. This has probably been going on for years, and it may keep getting worse over time. Just like a car engine damaged but still using the car without getting the engine repaired sooner or later in time the engine no longer functions the same with any organ of the body getting damaged by some long term condition. If your disease gets worse and worse over time, you could have kidney failure or some multi organ failure, depending on the condition causing this.
Regarding Chronic Kidney Failure the causes can be:
** Diabetes (uncontrolled diabetes (Type 1 or 2) for many years.
** High blood pressure for many years.
These are the top 2 causes of most chronic kidney disease. Controlling these diseases can help slow or stop the damage to the individual’s kidneys who has one of these, if not both.
Other common causes of chronic renal failure (CRF) include:
-recurring pyelonephritis (kidney infection)
-polycystic kidney disease (multiple cysts in the kidneys
-autoimmune disorders such as systemic lupus erythematosus.
-hardening of the arteries, which can damage blood vessels in the kidney.
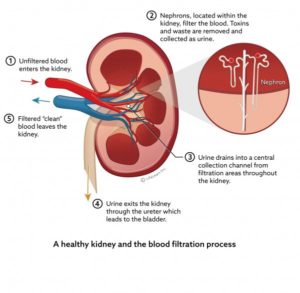
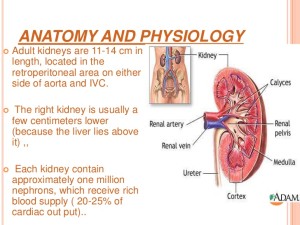
-A narrowed or blocked renal artery. A renal artery carries blood to the kidneys. Know this for starters, each of your kidneys has about a million tiny filters, called nephrons. The nephron is the tiny filtering structure in your kidneys. Each of your kidneys contain more than a million tiny filtering nephrons that help clean your blood removing toxins dumping them into your urinary bladder so you can evacuate them though urine (urea, urine; get it). Your nephrons play a vital role to our essential daily living. If over a long time you have a renal artery blocked the nephrons stop their function and die.
Remember the nephrons help all humans do the following if there kidneys or one kidney is functioning properly:
-Remove excess water, wastes (like urea, ammonia, etc.) & other substances from your blood.
-Return substances like sodium, potassium or phosphorus to the body whenever any of these substances run llow in your body or do the opposite if they run high to evacuate them through voiding dumping the sodium or phosphorus or potassium in the urinary bladder through the tube from the kidneys to the urinary bladder called ureters.
**If nephrons are damaged by the high sugar content or high blood pressure in the kidneys, they stop working. For a while, healthy nephrons can take on the extra work or overload. But if the damage continues, more and more nephrons shut down. After a certain point, the nephrons that are left cannot filter your blood well enough to keep you’re blood filtered properly to keep you healthy. Just like running from a bear in the street chancing you. We can run only so long but sooner or later we will run out of energy and not be able to run anymore, same concept for the kidney nephrons when they run out of enough energy due to the kidneys not properly working.**
The symptoms can be:
Urinate less than normal.
Have swelling and weight gain from fluid buildup in your tissues. This is called edema.
Feel very tired or sleepy.
Not feel hungry, or you may lose weight without trying.
Often feel sick to your stomach (nauseated) or vomit.
Have trouble sleeping.
Have headaches or trouble thinking clearly.
So what will you do GO TO A DOCTOR OR CALL 911 AND GO TO THE ER:
Your doctor will do blood and urine tests to help find out how well your kidneys are working. These tests can show signs of kidney disease and anemia. (You can get anemia from having damaged kidneys.) You may have other tests to help rule out other problems that could cause your symptoms.
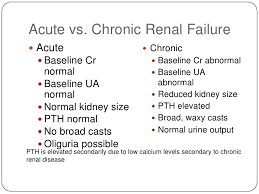
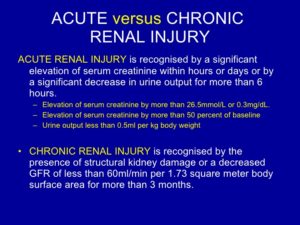
To diagnose chronic renal failure is pretty much the same tests that are listed above on acute renal failure plus:
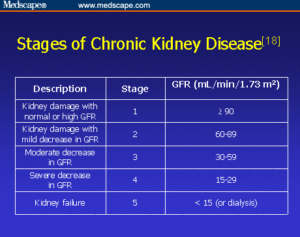
Chronic kidney disease is also called chronic renal failure or chronic renal insufficiency.There are five stages of kidney disease, from kidney damage with normal GFR to kidney failure. So GFR will help the MD rule out acute versus chronic to give the MD direction on Rx.Your doctor will ask questions about any past kidney problems. He or she will also ask whether you have a family history of kidney disease and what medicines you take, both prescription and over-the-counter drugs.
Diagnosis & Treatment (Rx) for Chronic Kidney (Renal) Failure (CRF):
There are things you can do to slow or stop the damage to your kidneys. Taking medicines and making some lifestyle changes can help you manage your disease, prevent further damage to the kidneys, if their functioning at all and make you possibly feel better.
Kidney disease is a complex problem. You will probably need to take a number of medicines and have many tests. To stay as healthy as possible, take your medicines just the way your doctor says to and work closely with your doctor.
Go to all your appointments for the MD to see a increase in function or decrease in function of your kidney or kidneys you have still functioning to a level. To do that you can’t just go every 6 months especially when first diagnosed with it or with a collapse of an exacerbation of kidney failure in a worse level that brought on new symptoms that brought you to the ER.
Lifestyle changes are an important part of your treatment. Taking these steps can help slow down kidney disease and reduce your symptoms. These steps may also help with high blood pressure, diabetes, and other problems that make kidney disease worse or made the kidney disease happen with the secondary diagnosis you had originally for years (ex. Hypertension or Diabetes if not both especially is uncontrolled)
Very hard, never a complete 100 % resolution. It is like emphysema done by smokers the damage is done or like a heart attack the area of the infarction=damage is already done to the heart muscle.
Scared now, understandable but unfortunately the damage is done, so its get the organ to its optimal level of functioning or replace the damaged kidney (s) through a transplant of one. You need to know this, do it if you want to live LONGER. Remember fear is fear itself, the fear run it over and deal with what you have and make your life longer & better! It’s all up to you. HANDSOME I know you can do it , I am there for you as a good friend and professional RN and I would love you to last longer John!! XO
You may have a test done that lets your doctor look at a picture of your kidneys, such as an ultrasound or CT (Cat Scan of the kidneys). These tests can help your doctor measure the size of your kidneys, estimate blood flow to the kidneys, and see if urine flow is blocked. In some cases, your doctor may take a tiny sample of kidney tissue (biopsy) to help find out what caused your kidney disease.
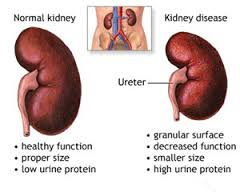
Chronic kidney disease is caused by damage of the kidneys whether the cause of it be primary a Renal or Kidney problem or a secondary, another disease or disorder that affects the kidneys in doing their job, like hyperglycemia related to a individual with uncontrolled diabetes, for instance.
Chronic kidney disease may seem to have come on suddenly. But it has been happening bit by bit for many years as a result of damage to your kidneys.
One way to measure how well your kidneys are working is to figure out your glomelular filtration rate (GFR). The GFR is usually calculated using results from your blood creatinine test.
Then the stage of kidney disease is figured out using the GFR (glomelular filtration rate). There are five stages of kidney disease, from kidney damage with normal GFR to kidney failure.
Your doctor will do tests that measure the amount of urea (BUN) and creatinine in your blood. These tests can help measure how well your kidneys are filtering your blood. As your kidney function gets worse, the amount of nitrogen (shown by the BUN test) and creatinine in your blood increases. The level of creatinine in your blood is used to find out the glomerular filtration rate (GFR). The GFR is used to show how much kidney function you still have. The GFR is also used to find out the stage of your kidney disease your in if you have it and its to guide decisions about treatment. *