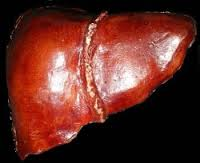
A. HEALTHY LIVER
B 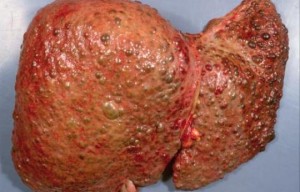
B. DISEASED LIVER
TREATMENT There are no medical treatments yet for NAFLD. Eating a healthy diet and exercising regularly may help prevent liver damage from starting or reverse it in the early stages.
- See a doctor who specializes in the liver regularly
- Talk to your doctor about ways to improve your liver health
- Lose weight, if you are overweight or obese
- Lower your cholesterol and triglycerides
- Control your diabetes
- Avoid alcohol
- PREVENTION There are ways to prevent NAFLD:
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Eat a healthy diet
- Exercise regularly
- Limit alcohol intak
- Only take medicines that you need and follow dosing recommendations. The more severe form of NAFLD is called non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). NASH causes the liver to swell and become damaged. NASH tends to develop in people who are overweight or obese, or have diabetes, high cholesterol or high triglycerides. NASH can occur in many.
- Causes: NASH:NASH affects 2 to 5 percent of Americans. An additional 10 to 20 percent of Americans have fat in their liver, but no inflammation or liver damage, a condition called “fatty liver.” Although having fat in the liver is not normal, by itself it probably causes little harm or permanent damage. If fat is suspected based on blood test results or scans of the liver, this problem is called nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). If a liver biopsy is performed in this case, it will show that some people have NASH while others have simple fatty liver.
- Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis or NASH is a common, often “silent” liver disease. It resembles alcoholic liver disease, but occurs in people who drink little or no alcohol. The major feature in NASH is fat in the liver, along with inflammation and damage. Most people with NASH feel well and are not aware that they have a liver problem. Nevertheless, NASH can be severe and can lead to cirrhosis, in which the liver is permanently damaged and scarred and no longer able to work properly.
- Most people with NASH are between the ages of 40 and 60 years. It is more common in women than in men. NASH often has no symptoms and people can have NASH for years before symptoms occur. NASH is one of the leading causes of cirrhosis in the United States. Up to 25% of adults with NASH may have cirrhosis. Know people have NASH even if they do not have one risk factor can get the disease.
- Both NASH and NAFLD are becoming more common, possibly because of the greater number of Americans with obesity. In the past 10 years, the rate of obesity has doubled in adults and tripled in children. Obesity also contributes to diabetes and high blood cholesterol, which can further complicate the health of someone with NASH. Diabetes and high blood cholesterol are also becoming more common among Americans.
-
- Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) is fat in the liver, with inflammation and damage.
- NASH occurs in people who drink little or no alcohol and affects 2 to 5 percent of Americans, especially people who are middle-aged and overweight or obese.
- NASH can occur in children.
- People who have NASH may feel well and may not know that they have a liver disease.
- NASH can lead to cirrhosis, a condition in which the liver is permanently damaged and cannot work properly.
- Fatigue can occur at any stage of NASH.
- Weight loss and weakness may begin once the disease is advanced or cirrhosis is present.
- NASH may be suspected if blood tests show high levels of liver enzymes or if scans show fatty liver.
- NASH is diagnosed by examining a small piece of the liver taken through a needle, a procedure called biopsy.
- People who have NASH should reduce their weight, eat a balanced diet, engage in physical activity, and avoid alcohol and unnecessary medications.
- No specific therapies for NASH exist. Experimental therapies being studied include antioxidants and antidiabetes medications.
- Other Pointers in knowing about the types of liver diseases:
- Most liver diseases are managed and not cured. The exception is for gallstone disease and some viral infections like Hepatitis A and infectious mononucleosis. All forms of liver disease has the ability to progress to cirrhosis and cause liver failure. Complications associated with cirrhosis and liver failure include an increased risk of bleeding and infection, malnutrition and weight loss, and decreased cognitive function.
- Depending on the type of cause for liver disease, determines how it is treated. Hep A requires supportive care from others to maintain hydration while the body’s immune system continues to fight off infections. Other diseases may require long-term care to control and minimize consequences of a particular disease. With cirrhosis and end-stage liver disease patients, they are often given medications to control the amount of protein absorbed in the diet. For other cirrhosis patients, they may not be able to metabolize waste products which raises their blood ammonia levels. To help them function, they need to take water pills (diuretics) and start a low sodium diet to minimize water retention. Only when all other options have failed is liver transplantation an option.
- Symptoms of liver disease range depending on the exact cause for the limited liver function. The general symptoms include a weakness or fatigue, weight loss, nausea, vomiting, fever and a yellow discoloration. If these symptoms are experienced without an explanation, it may be time to consult a medical professional. The time for education is before something like this happens. The survival rate is much higher for the individuals that seek medical attention early on through the act of having the knowledge to make the right decision. By the way the yellow discoloration is what we call Jaundice.
- Some of the other viruses that cause liver disease are viral infections like Mononucleosis, Adenovirus and Cytomegalovirus. There are also non-viral infections like toxoplasmosis and Rocky Mountain Spotted fever that could lead to liver disease but they are less common.
- There are other conditions like Hemachromatosis (iron overload), which is a metabolic disorder that leads to abnormally elevated amounts of iron that is stored in the body. It is an inherited disease. Wilson’s disease is another inherited disease but it affects the body’s ability to metabolize copper. Gilbert’s Disease is an abnormality in bilirubin metabolism in the liver and affects up to 7% of the North American population.
- Most people with NASH are between the ages of 40 and 60 years. It is more common in women than in men. NASH often has no symptoms and people can have NASH for years before symptoms occur. NASH is one of the leading causes of cirrhosis in adults in the United States. Up to 25% of adults with NASH may have cirrhosis. Know people have NASH even if they do not have one risk factor.
- Due to alcohol abuse acting as the most common cause of liver disease, it is recommended that alcohol consumption is in moderation. It may help minimize the risk of alcohol-related liver disease. Hepatitis B and C contraction can be decreased by minimizing the risk of exposure to another person’s bodily fluids. There is a vaccination available for Hepatitis A and B. There is screening available for Hepatitis C at most clinics or doctors offices. Fatty liver disease is preventable by the promotion of a healthy lifestyle. Those lifestyle choices include a well-balanced diet, weight control, avoiding excess alcohol consumption and routine exercise.