What is Sarcoma?
Sarcoma is a rare but deadly form of cancer affecting connective tissues such as fat, muscle, blood vessels, nerve, bone, deep skin and cartilage. There are roughly 15,000 new cases in the United States each year, with a very low median age of 36 (for bone sarcomas). Survival rates are low, even in comparison to other rare cancers. Rhabdomyosarcoma, a relatively common sarcoma, has a five-year survival rate of 65%, even if caught before metastasis. If caught after metastasis, the five-year survival rate lowers to approximately 30%. This is all to say that while sarcomas are rare, they are extremely devastating.
Sarcomas are a diverse and sporadic group of tumors that have minimal hereditary influence. They are generally classified into two major groups; the group of tumor-specific reoccurring genetic mutations via specific and aberrant chromosome translocation, and the group of non-reoccurring mutations which are based on severe genetic and chromosomal instability. Both groups have altered cell growth-factor signaling pathways. As a result, the introduction of drugs which can normalize growth-factor receptors and proteins are of great interest and the primary treatment given. With improvements in these drugs, it is believed that sarcoma can move from a deadly disease to a chronic but non-life-threatening disease.
Unfortunately, the specificity of the first group of sarcomas, where specific chromosomes are improperly translocated, can often permit the sarcoma to prevail after standard treatment. This is obviously problematic but, if overcome, could spark the development of a whole new field of cancer treatment. In other words, if scientists can discover how to isolate and guide specific chromosomal arrangement, they will able to address many of the hard to treat cancers of today.
With genetic engineering it is theoretically possible to prevent cancer before it begins. However, even without moving this far into the future, the improper chromosomal translocation can provide a sort of name-tagging of the cancer cell. With the cancer cells identified, it can guide modalities aimed at destroying diseased tissue while sparing healthy tissue.
Sarcoma is an under-researched cancer whose research can help to elevate cancer treatment, as a whole. Not only would breakthroughs save the lives of countless children, it could also advance medicine, as a whole. By bringing awareness to sarcoma and the potential development its research can spark, this potential can become a reality.
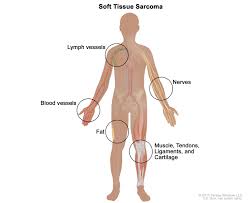
Soft tissue sarcomas may develop in any tissue that connects, supports or surrounds other structures and organs in the body. Some examples of where soft tissues sarcomas can develop are muscles, fascia (the tough membrane that surrounds muscles), tendons, fat, blood vessels, nerves and synovial tissues (connective tissue that makes up the membranes surrounding joints).
Soft tissue sarcomas are rare in adults, accounting for less than 1 percent of all new cases of cancer. The American Cancer Society reports that about 12,750 new cases of soft tissue sarcoma will be diagnosed in 2019 (7,240 cases in males and 5,510 cases in females). Sarcomas can be found almost anywhere in the body.
According to the National Cancer Institute, about 50 percent of soft tissue sarcoma cases occur in the extremities (arms and legs), 40 percent occur in the trunk (back and chest), and 10 percent occur in the head and neck.
Causes of Sarcoma:
The American Cancer Society states the following on causes of Sarcoma:
“Scientists don’t know exactly what causes most soft tissue sarcomas , but they have found some risk factors that can make a person more likely to develop these cancers. And research has shown that some of these risk factors affect the genes in cells in the soft tissues.
Researchers have made great progress in understanding how certain changes in DNA (pieces of genes) can cause normal cells to become cancer. DNA carries the instructions for nearly everything our cells do. We usually look like our parents because they are the source of our DNA. But DNA affects more than just the way we look.
The DNA is made of genes. Genes carry the recipes for making proteins, the molecules that control all cell functions. Some genes contain instructions for proteins that control when our cells grow and divide.
- Certain genes that promote cell division are called oncogenes.
- Others that slow down cell division or cause cells to die at the right time are called tumor suppressor genes.
Cancers can be caused by DNA mutations (defects) that turn on oncogenes or turn off tumor suppressor genes.
Many family cancer syndromes have been found in which inherited DNA mutations cause a very high risk of developing breast, colon, kidney, eye, or other cancers. Some of these syndromes are also linked to an increased risk of developing soft tissue sarcomas.
DNA mutations in soft tissue sarcoma are common. But they’re usually acquired during life rather than having been inherited before birth. Acquired mutations may result from exposure to radiation or cancer-causing chemicals. In most sarcomas, they occur for no apparent reason.
Researchers still don’t know why most soft tissue sarcomas develop in people who have no apparent risk factors.”