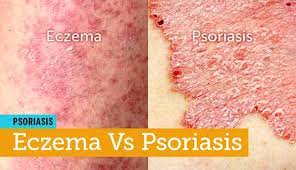
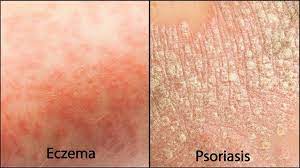
If you suffer from itchy, red and dry skin you’ve probably tried every cream, ointment and lotion on the market to treat your eczema. But if you’ve tried it all and can’t seem to calm your itchy skin it might be because there’s another skin condition that can have visually similar symptoms and your eczema cream probably won’t work for it. It’s called psoriasis.
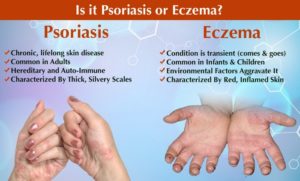
Eczema and psoriasis are like twins — they have a similar look, but deep down, they are fundamentally different.
So What is the difference?
If you suffer from itchy, red and dry skin you’ve probably tried every cream, ointment and lotion on the market to treat your eczema. But if you’ve tried it all and can’t seem to calm your itchy skin it might be because there’s another skin condition that can have visually similar symptoms and your eczema cream probably won’t work for it. It’s called psoriasis.
Eczema and psoriasis are like twins — they have a similar look, but deep down, they are fundamentally different!
You might be thinking: When you’ve got an irritating, itchy spot, who cares about the subtle difference? But this can help you and your dermatologist decide which skin condition you are having.
Dr. Millstein, a physician at Penn Internal Medicine Woodbury Heights, says “Psoriasis tends to cause milder itching and, in some less common types of psoriasis, a terrible burn. Eczema, on the other hand, can lead to very intense itching. When it starts to become severe, some people scratch their skin so hard that it bleeds.”
Both skin diseases can show up anywhere on your body, but they have their own favorite areas.
Psoriasis causes troubles commonly on the:
- Scalp
- Elbows
- Knees
- Buttocks
- Face
Eczema can occur in those places, but it most often inflames the skin on the back of the knees or the inside of the elbows.
Although you can get either disease at any age, eczema often affects children while psoriasis usually manifests in early adulthood or later.
3. Sunshine Can Ease Psoriasis But Not Necessarily Eczema
If you have eczema, summer might not be your favorite season. Some people with eczema are sensitive to heat. In hot weather, overheating can cause perspiration, which can lead to skin flare.
“However, for most psoriasis patients, abundant natural ultraviolet B (UVB) light from sunshine can be a blessing. UVB light can slow down the abnormal growth of skin cells. It is used as a medical treatment for psoriasis,” says Dr. Millstein.
But remember, too much of a good thing can become damaging. If you go sunbathing without using sunscreen or are exposed to sunlight for too long, overexposure can trigger psoriasis symptoms. If you start to feel itchy or see red spots, get out of the sun. Make sure to talk to your dermatologist about the best amount of time for exposure to the sun.
Finding Treatment
If you have itchy, red patches on any part of your body that don’t go away with over-the-counter medications, it’s better to see a dermatologist directly. Primary care providers can also help make a diagnosis and manage your symptoms, but a dermatologist has specialized training and extensive experience in recognizing subtleties of the two skin conditions.
The treatments for eczema and psoriasis are similar. Some of the common treatments include:
- Over-the-counter relief: Many of these products are aimed to help relieve symptoms or prevent infection.
- Topicals: These are medications your doctor prescribes for you to apply on the affected skin. skin products (like moisturizing emollients and topical corticosteroids), prescription skin products, avoiding triggers, and having a good skin care regimen and healthy lifestyle. Skin products are particularly good for calming eczema or psoriasis flares.
- Phototherapy: Also known as light therapy, phototherapy uses a machine to create UVB light/light therapy with ultraviolet. Phototherapy is safe — you will only be exposed to a healthy, controlled amount of UVB light, and the procedure is performed under medical supervision. This can reduce itching and inflammation, and boost bacteria-fighting ability of the skin.
- Biologics: These are medications that can target the protein that makes you have the inflammation response. They’re usually given by injection or intravenous (IV) infusion. Other medications that broadly suppress the immune system, whether oral or to be applied to the skin, can work for both. Topical steroids have been the workhorse treatment for both psoriasis and eczema. However, newer agents that are more ‘targeted’ to the now-known underlying cause of these two inflammatory disorders are more specific for psoriasis or eczema by suppressing specific arms of the immune system.
- Systemics: These are medications you can take by mouth to control your immune system response and reduce inflammation. It’s often prescribed to you if your condition is severe.
Eczema and psoriasis can present very differently in each person. Comparing your symptoms to another patient’s won’t always give you the right answer or the best solution for another.
In severe cases, psoriasis can turn into psoriatic arthritis. When this is the case, a medicine such as methotrexate or cyclosporine may be recommended by a doctor to help manage symptoms. Be sure to ask about all potential ointments and creams available to help your skin rashes.
Clearly, there’s a lot more to the psoriasis vs. eczema question than meets the eye. But regardless of which condition you have, or think you have, the is always one answer on who to go to. Talk to the right expert being a dermatologist about getting the right diagnosis and treatment would help you if you want the best treatment. Always go to a specialist with the problem you have as opposed to a general practictioner (GP)especially if they you do go to their GP and the problem does not resolve with their choice of an treatment. If your insurance needs for you to go to a specialist with a consult, he or she that is your GP can always do that if you request it if the GP has not recommended it yet!
(updated 5/12/24)