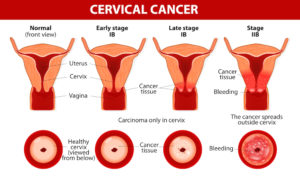
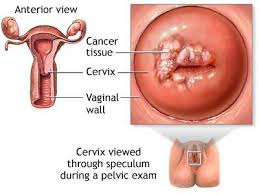
National Folic Acid Awareness of Month, which was in the beginning of this month! For those who may have missed the info on it don’t fret striveforgoodhealth is covering Folic acid today and its especially important to women who might become pregnant, as it can help prevent serious birth defects of the brain, neck and spine. Recent studies suggest that it can also help lower the risk of neural tube defects and orofacial clefts (cleft lip and palate). Notably, folic acid has been shown to lower the risk of anencephaly (the absence of a large part of the brain and skull) and spina bifida (an opening in the spinal column) by 50 to 70%.
Much of the baby’s growth and development happens very early in pregnancy, even before most women know they’re pregnant. Experts estimate that women need to start taking folic acid at least one month before they become pregnant for it to prevent birth defects, so it’s important to make folic acid-enriched foods and vitamins a part of your daily routine.
The benefits aren’t limited to your baby: your body needs folic acid, too. The acid helps to create healthy new cells in the body, from hair to nails to skin and blood cells. Without it, blood cells become unstable, and the body is susceptible to disease. The vitamin also protects your liver, allowing it to continue purifying your body. Folic acid is a water-soluble vitamin that your body cannot store, so it should be taken every day to replenish your body’s supply.
Many foods are now being fortified with more folic acid, such as grains, pastas and breakfast cereals. Check the nutritional facts label on your favorite products to see how much they contain. Many cereals now contain as much as 100% of the recommended daily value. Additionally, prenatal vitamins typically contain folic acid. If you’re not yet taking a prenatal vitamin, you can also look for multivitamins with added acid, or buy folic acid pills.
Birth defects are common, costly, and critical conditions that affect one in every 33 U.S. newborns annually. Women can reduce their risk of having a baby born with a birth defect by making healthy choices and adopting healthy habits before and during pregnancy.
Health care providers can encourage parents-to-be to make a PACT for birth defects prevention by taking the following steps: Planning ahead for pregnancy; Avoiding harmful substances like chemicals in the home or workplace (2); Choosing a healthy lifestyle, including eating a healthy diet (3); and Talking with their health care provider before and during pregnancy, particularly about medication use.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention encourages health care providers to become active participants in National Birth Defects Prevention Month by joining the nationwide effort to raise awareness of birth defects, their causes, and their impact.
CDC urges all women of childbearing age who can become pregnant to get 400 µg of folic acid every day to help reduce the risk for neural tube defects. Health care providers should encourage women of childbearing age to consume folic acid in fortified foods or supplements, or a combination of the two, in addition to a diet rich in folate CDC urges all women of childbearing age who can become pregnant to get 400 µg of folic acid every day to help reduce the risk for neural tube defects. Health care providers should encourage women of childbearing age to consume folic acid in fortified foods or supplements, or a combination of the two, in addition to a diet rich in folate.
An easy way to be sure you’re getting enough folic acid is to take a daily multivitamin with folic acid in it. Most multivitamins have all the folic acid you need. If you get an upset stomach from taking a multivitamin, try taking it with meals or just before bed. If you have trouble taking pills, you can try a multivitamin that is gummy or chewable. Also be sure to take it with a full glass of water.
Folic acid has been added to foods such as enriched breads, pastas, rice and cereals. Check the Nutrition Facts label on the food packaging. A serving of some cereals has 100% of the folic acid that you need each day.
In addition to getting 400 mcg of folic acid from supplements and fortified foods, you can eat a diet rich in folate. You can get food folate from beans, peas and lentils, oranges and orange juice, asparagus and broccoli, and dark leafy green vegetables such as spinach, and mustard greens.
Nutritional habits
Although all enriched cereals and grain products in the U.S. are fortified with the B-vitamin folic acid, only one-third of U.S. women of childbearing age consume the recommended amount from their diet. Taking a multivitamin with folic acid every day is a key way that women can get the recommended amount of 400 mcg.
Be prepared before pregnancy
Women need folic acid, even if not planning to become pregnant, since 50% of all pregnancies are unplanned. Taking folic acid before pregnancy reduces the risk of birth defects of the brain and spine, called neural tube defects (NTDs), by up to 70%.
Message to the Hispanic community
Hispanic babies are 1.5 to 2 times more likely than others in the U.S. to be born with an NTD. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) report that Latinas in the U.S. consume the least amount of folic acid and have the least knowledge about folic acid among racial or ethnic groups.