The skin is the largest organ of your body. It acts as a barrier between invaders (pathogens) and your body. Skin forms a waterproof mechanical barrier. Microorganisms that live all over your skin can’t get through your skin unless it’s broken. The skin and mucous membranes act as a physical barrier preventing penetration by microbes. If the skin is cut then the blood produces a clot which seals the wound and prevents microbes from entering.
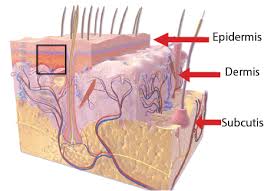
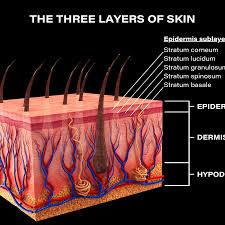
There are layers of skin and the first five layers form the epidermis, which is the outermost, thick layer of the skin and is listed above in the pictures. Notice in the second picture on the Rt. shows all blood vessels below epidermis.
All seven layers vary significantly in their anatomy and function.
It is made up of three main layers, the epidermis, dermis, and the hypodermis, all three varying significantly in their anatomy and function. The skin’s structure is made up of an intricate network which serves as many functions for the body’s initial barrier against pathogens, UV light, and chemicals, and mechanical injury. It also maintains body temperature and prevents water loss from the body.
Of all the organs in the human body, few take the pounding your skin does. Yes, your skin is an organ, your body’s largest, in fact, and among your most important, considering you cannot live without it.
Your skin is a biological marvel capable of performing remarkable functions every day. It protects your muscles and organs from outside threats. It endures bumps and bruises, cuts and scratches, the sun’s burning rays and the grime left by dirt and dust. It moves and stretches when you do and mostly bounces back to form when you’re still.
Even when your body is at rest, your skin is a bustle of cellular activity. Basal cells change shape as they move to the surface to replace dying squamous cells. Merkel cells help your nerves sense the touch of another. Melanocytes produce melanin, the skin-darkening pigment that protects your skin from the sun.
And like other organs, your skin may develop cancer.
Skin cancer:
Skin cancer is the abnormal growth of skin cells — most often develops on skin exposed to the sun. But this common form of cancer can also occur on areas of your skin not ordinarily exposed to sunlight.
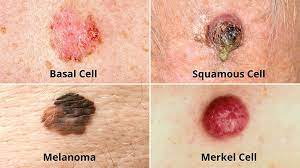
There are three major types of skin cancer — basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma and melanoma.
You can reduce your risk of skin cancer by limiting or avoiding exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation. Checking your skin for suspicious changes can help detect skin cancer at its earliest stages. Early detection of skin cancer gives you the greatest chance for successful skin cancer treatment.
The first 2 types of skin cancer, which are:
1.Basal Cell Carcinoma 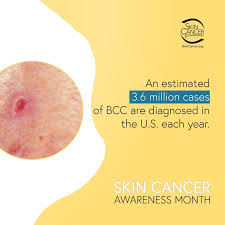
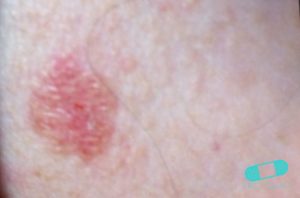
Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is the most common form of skin cancer and the most frequently occurring form of all cancers. In the U.S. alone, an estimated 3.6 million cases are diagnosed each year. BCCs arise from abnormal, uncontrolled growth of basal cells. Basal Cell Carcinoma grows slowly, most are curable and cause minimal damage when caught and treated early.
Knowing the causes, risk factors and warning signs can help you detect them early, when they are easiest to treat and cure.
The risk factors of BCC are:
–UV exposure from the sun or indoor tanning.
-History of skin cancer, including squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) or melanoma
– Age over 50: Most BCCs appear in people over age 50.
-Fair skin: People with fair skin have an increased risk.
-Male gender: Men are more likely to develop BCC.
-Chronic infections and skin inflammation from burns, scars and other conditions.
Warning Signs can help with early detection and treatment, almost all basal cell carcinomas (BCCs) can be successfully removed without complications. Look out for any new, changing or unusual skin growths, so you can spot skin cancers like BCC when they are easiest to treat and cure.
IT’S A FACT 90% of nonmelanoma skin cancers (mainly BCCs and SCCs) are associated with exposure to UV radiation from the sun.
Treatments for BCC:
When detected early, most basal cell carcinomas (BCCs) can be treated and cured. Prompt treatment is vital, because as the tumor grows, it becomes more dangerous and potentially disfiguring, requiring more extensive treatment. Certain rare, aggressive forms can be fatal if not treated promptly.
If you’ve been diagnosed with a small or early BCC, a number of effective treatments can usually be performed on an outpatient basis, using a local anesthetic with minimal pain. Afterwards, most wounds can heal naturally, leaving minimal scarring.
Options include:
- Curettage and electrodesiccation (electrosurgery)
- Mohs surgery
- Excisional surgery
- Radiation therapy
- Photodynamic therapy
- Cryosurgery
- Laser surgery
- Topical medications
- Medications for advanced BCC
2. Melanoma – worst cancer the deepest in skin 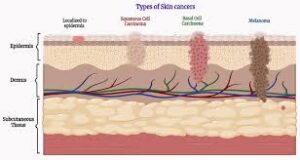
Melanoma is a type of cancer that usually begins in the skin. Specifically, it begins in cells called melanocytes. These are cells that produce melanin. Melanin is the pigment that gives skin, hair, and eyes their color.
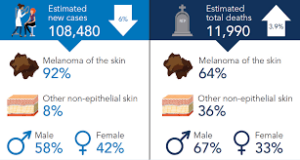
Melanoma is among the most serious forms of skin cancer.
Melanoma is the deadliest type of skin cancer. It can be “in situ” which means that the cancer is confined to the top layer of skin, thus being highly curable. It can also be “malignant” which means that the cancer can spread to other parts of the body which significantly decreases the survivability rate. Melanoma in situ can grow to be malignant melanoma if not treated. The key to surviving melanoma is early detection, and especially before it becomes malignant. Melanoma caught in the early stages of its development is highly curable with a 97% survival rate.
Risk Factors of Melanoma are:
-Ultraviolet light exposure
-Moles
-Fair skin, freckling, light hair
-Family history of melanoma
-Personal history of melanoma or skin cancers
-Having a weakened immune response
-Being older
-Being male
-Xeroderma pigmentosum (XP): This is a rare, inherited condition that affects skin cells’ ability to repair damage to their DNA. People with XP have a high risk of developing melanoma and other skin cancers when they are young, especially on sun-exposed areas of their skin.
Again warning signs can count help with early detection and treatment this can be successfully removed without complications. Look out for any new, changing or unusual skin growths, so you can spot skin cancers like BCC when they are easiest to treat and cure.
IT’S A FACT Only 20-30% of melanomas are found in existing moles. While 70-80% arise on normal-looking skin.
Treatments vary depending on the stage its in:
Stage I melanoma:
Stage I melanomas have grown into deeper layers of the skin, but they haven’t grown beyond the area where they started.
These cancers are typically treated by wide excision (surgery to remove the tumor as well as a margin of normal skin around it). The width of the margin depends on the thickness and location of the melanoma. Most often, no other treatment is needed.
Some doctors may recommend a sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) to look for cancer in nearby lymph nodes, especially if the melanoma is stage IB or has other traits that make it more likely to have spread. You and your doctor should discuss this option.
If the SLNB does not find cancer cells in the lymph nodes, then no further treatment is needed, although close follow-up is still important.
If cancer cells are found on the SLNB (which changes the cancer stage to stage III – see below), a lymph node dissection (removal of all lymph nodes near the cancer) might be recommended. Another option might be to watch the lymph nodes closely by getting an imaging test such as ultrasound of the nodes every few months.
If the SLNB found cancer, adjuvant (additional) treatment with immune checkpoint inhibitors or targeted therapy drugs (if the melanoma has a BRAF gene mutation) might be recommended to try to lower the chance the melanoma will come back. Other drugs or perhaps vaccines might also be options as part of a clinical trial.
Stage II melanoma:
This stage II skin melanoma have grown deeper into the skin than stage I melanomas, but they still haven’t grown beyond the area in the skin where they started.
Wide excision (surgery to remove the melanoma and a margin of normal skin around it) is the standard treatment for these cancers. The width of the margin depends on the thickness and location of the melanoma.
Because the melanoma may have spread to nearby lymph nodes, many doctors recommend a sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) as well. This is an option that you and your doctor should discuss.
If a SLNB is done and does not find cancer cells in the lymph nodes, then sometimes no further treatment is needed, but close follow-up is still important.
For certain stage II melanomas, the immune checkpoint inhibitor pembrolizumab (Keytruda) might be given after surgery to help reduce the risk of the cancer returning. Radiation therapy to the area might be another option, especially if the melanoma has features that make it more likely to come back.
If the SLNB finds that the sentinel node contains cancer cells (which changes the cancer stage to stage III – see below), then a lymph node dissection (where all the lymph nodes in that area are surgically removed) might be recommended. Another option might be to watch the lymph nodes closely with an imaging test such as ultrasound of the nodes every few months.
Whether or not the lymph nodes are removed, adjuvant (additional) treatment with immune checkpoint inhibitors or targeted therapy drugs (if the melanoma has a BRAF gene mutation) might be recommended to try to lower the chance the melanoma will come back. Other drugs or perhaps vaccines might also be options as well as part of a clinical trial.
Your doctor will discuss the best options with you depending on the details of your situation.
Stage III Melanoma:
These cancers have spread to nearby areas in the skin or lymph vessels, or they have reached the nearby lymph nodes.
Surgical treatment for stage III melanoma usually requires wide excision of the primary tumor as in earlier stages, along with a lymph node dissection (where all the nearby lymph nodes are surgically removed).
After surgery, (additional) adjuvant treatment with immune checkpoint inhibitors or with targeted therapy drugs (for cancers with BRAF gene changes) may help lower the risk of the melanoma coming back. Other drugs or perhaps vaccines may also be recommended as part of a clinical trial to try to reduce the chance the melanoma will come back. Another option is to give radiation therapy to the areas where the lymph nodes were removed, especially if many of the nodes contain cancer.
If melanoma tumors are found in nearby lymph vessels in or just under the skin (known as in-transit tumors), they are removed, if possible. Other options might include injections of the T-VEC vaccine (Imlygic), interleukin-2 (IL-2), or Bacille Calmette-Guerin (BCG) vaccine directly into the melanoma; radiation therapy; or applying imiquimod cream. For melanomas on an arm or leg, another option might be isolated limb perfusion or isolated limb infusion (infusing just the limb with chemotherapy). Other possible treatments might include targeted therapy drugs (for melanomas with a BRAF or C-KIT gene change), immunotherapy, or chemotherapy.
Some stage III melanomas might be hard to cure with current treatments, so taking part in a clinical trial of newer treatments might be a good option.
Treating stage IV melanoma:
Stage IV melanomas have already spread (metastasized) to other parts of the body, such as distant lymph nodes, areas of skin, or other organs.
Skin tumors or enlarged lymph nodes causing symptoms can often be removed by surgery or treated with radiation therapy.
If there are only a few metastases, surgery to remove them might sometimes be an option, depending on where they are and how likely they are to cause symptoms. Metastases that can’t be removed may be treated with radiation or with injections of the T-VEC vaccine (Imlygic) directly into the tumors. In either case, this is often followed by adjuvant treatment with medicines such as immunotherapy or targeted therapy drugs.
The treatment of widespread melanomas has changed in recent years as newer forms of immunotherapy and targeted drugs have been shown to be more effective than chemotherapy.
Immunotherapy drugs called checkpoint inhibitors are often the first treatment. These drugs can shrink tumors for long periods of time in some people. Options might include:
- Pembrolizumab (Keytruda) or nivolumab (Opdivo) alone
- Nivolumab combined with relatlimab (Opdualag)
- Nivolumab or pembrolizumab, plus ipilimumab (Yervoy)
Combinations of checkpoint inhibitors seem to be more effective, although they’re also more likely to result in serious side effects, especially if they contain ipilimumab.
People who get any of these drugs need to be watched closely for serious side effects.
In about half of all melanomas, the cancer cells have BRAF gene changes. These melanomas often respond to treatment with targeted therapy drugs – typically a combination of a BRAF inhibitor and a MEK inhibitor. However, the immune checkpoint inhibitors mentioned above are often tried first, as this seems to be more likely to help for longer periods of time. Another option might be a combination of targeted drugs plus the immune checkpoint inhibitor atezolizumab (Tecentriq).
While immunotherapy is often used before targeted therapy, there might be situations where it makes sense to use targeted therapy first. For example, the targeted drugs are more likely to shrink tumors quickly, so they might be preferred in cases where this is important. In either case, if one type of treatment isn’t working, the other can be tried.
A small portion of melanomas have changes in the C-KIT gene. These melanomas might be helped by targeted drugs such as imatinib (Gleevec) and nilotinib (Tasigna), although these drugs often stop working eventually.
Rarely, melanomas might have changes in other genes such as NRAS, ROS1, ALK, or the NTRK genes, which can be treated with targeted drugs.
Immunotherapy using other medicines might be an option if immune checkpoint inhibitors or other treatments aren’t working. Options might include:
- Interleukin-2 (IL-2) (also known as aldesleukin)
- Lifileucel (Amtagvi), a type of tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte (TIL) therapy
These treatments can cause serious side effects in some people, so they are usually given in the hospital.
Chemotherapy (chemo) can help some people with stage IV melanoma, but other treatments are usually tried first. Dacarbazine (DTIC) and temozolomide (Temodar) are the chemo drugs used most often, either by themselves or combined with other drugs. Even when chemo shrinks these cancers, the cancer usually starts growing again over time.
It’s important to carefully consider the possible benefits and side effects of any recommended treatment before starting it.
Because stage IV melanoma is often hard to cure with current treatments, people may want to think about taking part in a clinical trial. Many studies are now looking at new targeted drugs, immunotherapies, and combinations of different types of treatments. (See What’s New in Melanoma Skin Cancer Research?)