Symptoms:
Some of the symptoms of this disease atrial fibrillation RVR include Chest Pain or Discomfort, heart palpitations (described as unnoticed skipped beats or skipped beats noticed from experienced dizziness or difficulty in breathing), shortness of breath when lying flat (orthopnea), shortness of breath (dyspnea after exertion) sudden onset of short breath during the night (also called paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea) and gradual swelling of lower extremities. As a result of inadequate blood flow, some patients complain of light headedness or dizziness and may feel like they are about to faint, a condition referred to as presyncope and may actually lose consciousness (syncope). Some patients experience respiratory distress that results in them appearing blue. A close examination of jugular veins usually reveals elevated pressure in some patients (jugular venous distention). When some patients are subjected to lung examinations, crackles and rales may be observed pointing to possible lung edema.
Importance of proper diagnosis:
A good diagnosis of the symptoms shown by patients is important to ascertain that the patient is suffering from atrial fibrillation with RVR. This is because some forms or irregular and rapid heart rates, tachyarrhythmia, are dangerous and must be ruled out as they are life threatening – such as ventricular tachycardia. Some patients are usually placed on continuous cardio respiratory monitoring, but an electrocardiogram ECG is vital for correct diagnosis.
How is it diagnosed?
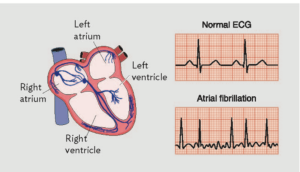
Simple, a typical 12 lead electrocardiogram (ECG). This test shows cardiac rhythms which atrial fibrillation is. Rhythms are made up of types of waves that the ECG shows which are P waves, QRS waves, T waves and U waves.
The QRS complexes should be narrow, to signify that they are being initiated by normal conduction of atrial electrical activity through the Intra-ventricular conduction system, or heart conduction system. Wide QRS complexes could point to ventricular tachycardia, although wide complexes may also be an indication of disease processes in the Intra-ventricular conduction system. The R-R internal will also likely be irregular. Meaning measuring from each R section of the QRS rhythm. It is also important to find out if there are triggering causes for the tachycardia which include dehydration, Hypovolemia – a decrease in blood volume, and more specifically decrease in blood plasma volume. You can go ahead to eliminate Acute coronary syndrome – which refers to any diseases that are directly attributed to the obstruction of coronary arteries.
How A Fib is treated:
1-A Shock
This is known as cardioversion and is used typically either when an immediate result is required or used when the Afib is of relatively recent onset or only intermittent, and so has more chance of staying in normal rhythm. In cardioversion a small shock is given using defibrillation pads. It is done under light anesthesia therefore it doesn’t hurt. The Afib may return however.
2-Rate Control Drugs
The biggest problem in Afib with RVR is too fast a heart rate. In a rhythm control strategy we use drugs such as beta-blockers to slow the heart rate down. These drugs typically will leave the patient in AF. For many people with AF it turns out that a rate control strategy is preferred as it is considered less risky than the rhythm control drugs used to get rid of the AF while being just as effective. In Afib with RVR rate control drugs can often slow the heart rate down fairly quickly and improve symptoms.
b-Rhythm Control Drugs
These medications are generally more powerful than the rate control drugs and attempt to convert the Afib back in to a normal rhythm. They are often given after a shock treatment to try and help the heart stay in normal rhythm. These drugs are also commonly used in hospitalized Afib with RVR patients. The problem with these drugs is that they may have side effects and associated risks. Many patients simply cannot tolerate Afib even if the rate is controlled and therefore require rhythm control drugs. They may be safe and effective however if used in selected patients. In cases of Afib with RVR these medications may need to be used if patients cannot tolerate other rate control medications.
3-Ablation Procedures
Ablation procedures are minimally invasive procedures typically done through the groin. They are typically used in patients that have tried, or cannot tolerate medicines for control of AFib. Ablation is typically not used as an emergency treatment of Afib with RVR, rather it is used for stable patients in AF, or those with intermittent AFib that wish to remain in normal rhythm. In patients that have had persistent Afib for a long time these procedures are not likely to be successful in the long term.
b-Pacemaker
This is typically the last throw of the dice for AF control. In some patients, drugs can either not control the rate in AFib with RVR, or the drugs can simply not be tolerated. In these patients who have no other choice, and in whom it is determined the Afib is causing harmful effects, a procedure called AV node ablation and pacemaker is done. In a relatively minor procedure, a small burn is made to the connection that connects the top and bottom chambers of the heart. A pacemaker is then inserted. This prevents Afib with RVR as although the top chambers continue to fire at a fast rate, the pacemaker now controls the bottom chamber, in a nice regular way. The downside of course is that now although the patient cannot have Afib with RVR, they have a pacemaker.
Acute afib RVR patients are more likely to be converted to Normal Sinus Rhythm (the best rhythm you could be in) as opposed to patients with chronic afib. There are complete resolutions for both kind of afib but atrial fibrillation in RVR the heart can handle for only so long and remembering the engine of our body is the heart so take good care of it for if you don’t it could allow you to die.